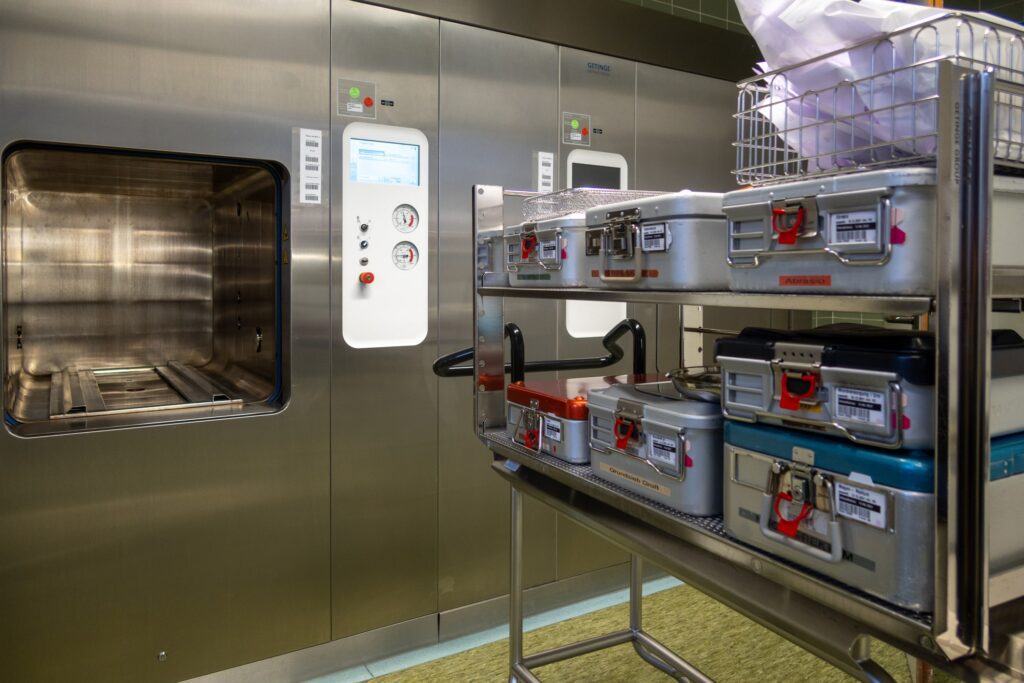
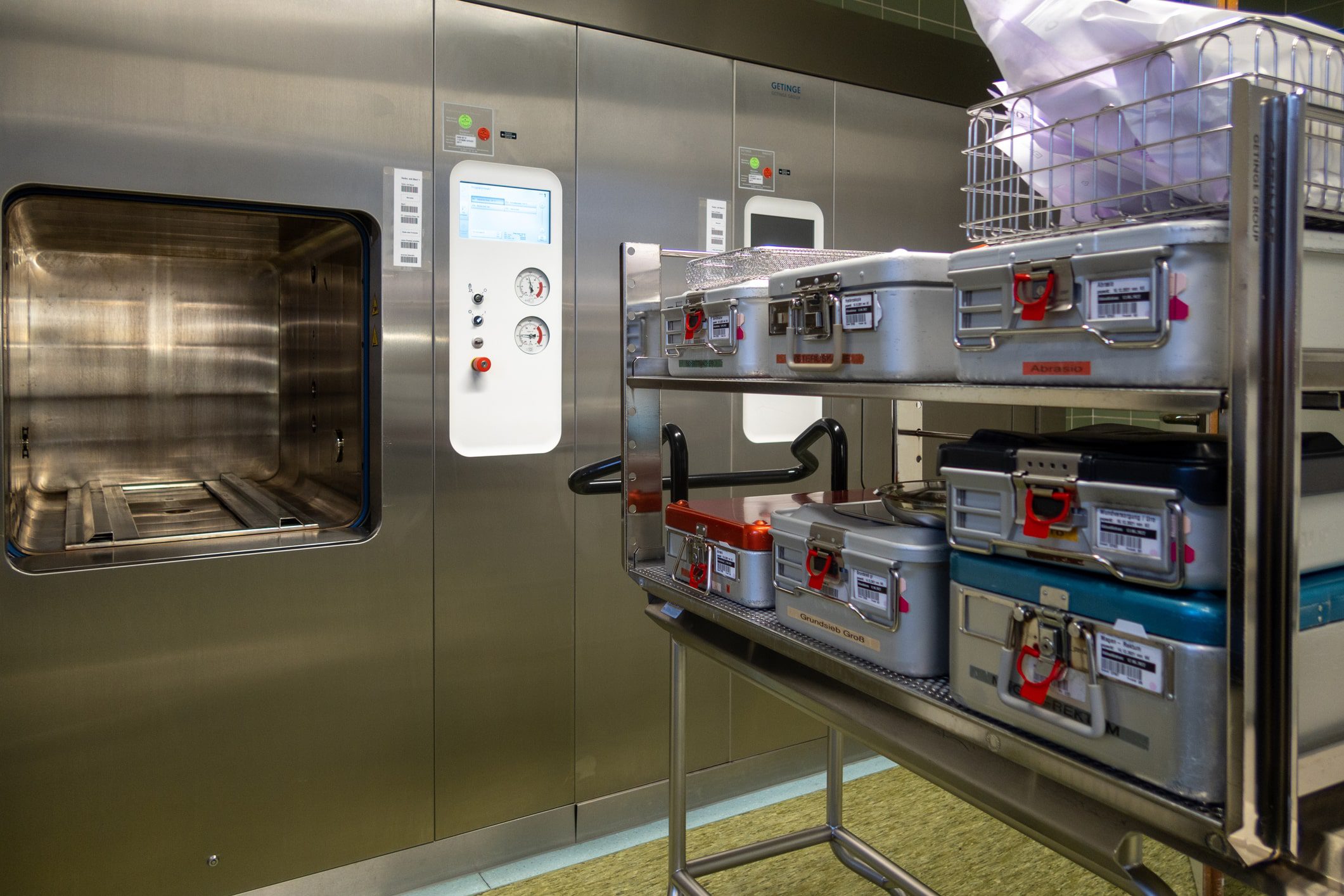
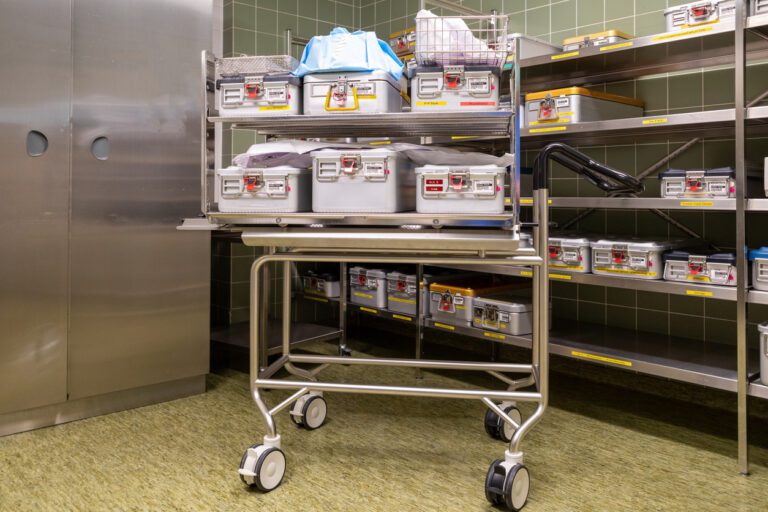
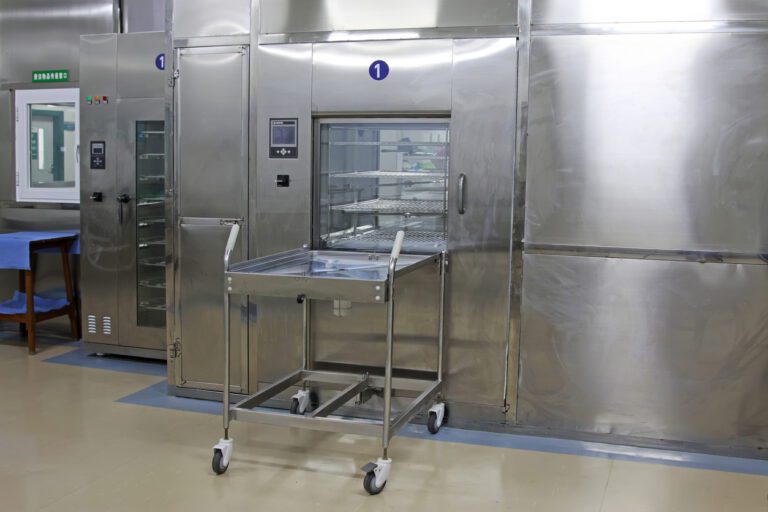
Welcome to the world of sterile processing departments, also known as SPDs. These crucial departments can be found in healthcare facilities and are responsible for keeping medical instruments clean, sterilized, and safe.
They monitor surgical supplies, instruments, and even some medical equipment closely. The SPD staff’s meticulous attention to detail plays a vital role in preventing infections and cross-contamination. Their tireless efforts include using sterilizers and ensuring proper storage of surgical supplies, all in the name of protecting patients’ health.
Sterile processing departments (SPDs) are highly regulated places that require specialized training. They have storage areas for surgical supplies, temperature-controlled rooms for sterilizers, and dedicated staff who carefully clean, disinfect, sterilize, and organize medical instruments.
The significance of these departments cannot be overstated. They play a vital role in maintaining the highest standards of patient care.
In this blog post, we will explore the rigorous processes involved in sterilizing medical instruments, including using a sterilizer. We will also discuss the critical role that Sterile Processing Departments (SPDs) play in preventing healthcare-associated infections by ensuring proper sterilization of medical supplies and instruments.
Table of Contents
- 0.1 What You Need to Know
- 0.2 Vital Role of the Sterile Processing Department in Healthcare
- 0.3 Why is the sterile processing department important?
- 0.4 Essential Equipment for Sterile Processing Department
- 0.5 Basics of Sterile Processing
- 0.5.1 Sterilization Eliminates All Microorganisms from Instruments and Equipment
- 0.5.2 Common Sterilization Methods Include Steam, Ethylene Oxide, and Hydrogen Peroxide
- 0.5.3 Proper Cleaning Is Essential Before Sterilization to Remove Debris or Organic Matter
- 0.5.4 Validation Processes Are Used to Ensure Effectiveness of Sterilization Cycles
- 0.6 Packaging and Sterilization Methods
- 0.7 Instrument Lifecycle Management
- 0.8 Key Factors for Ensuring Patient Safety in SPD
- 0.9 Conclusion
- 0.10 Frequently Asked Questions?
- 0.10.1 How often should medical instruments be sterilized?
- 0.10.2 What happens if an instrument is not properly sterilized?
- 0.10.3 Can I trust that all medical facilities have reliable sterile processing departments?
- 0.10.4 How can I ensure the safety of the medical instruments used on me?
- 0.10.5 Are there any risks associated with reusable medical instruments?
- 1 Subscribe to our Newsletter
What You Need to Know
The sterile processing department, or the Central Sterile Services Department (CSSD), plays a vital role in healthcare facilities. They are responsible for cleaning, disinfecting, packaging, sterilizing, and storing medical instruments and equipment in the sterilizer room or area. This process involves multiple steps to sterilize the instruments and maintain the highest level of sterility using the best sterilization techniques.
Multiple Steps
Sterile processing involves a series of essential steps to ensure the safety and efficacy of medical instruments, including using a sterilizer and EO gas. Each day, these instruments are carefully processed and sterilized to eliminate any potential contaminants.
It is extremely important to keep medical equipment clean and sterile. The sterile processing department plays a vital role in this process by following a series of steps, including cleaning, disinfecting, packaging, sterilizing, and storing the equipment.
- Cleaning: The first step involves thoroughly cleaning the instruments to remove any visible debris or contaminants. This is typically done using specialized cleaning agents and equipment.
- Disinfection: After cleaning, the instruments undergo a disinfection process to eliminate any remaining microorganisms that may pose a risk to patients. Different disinfection methods may be employed depending on the instrument’s material and intended use.
- Packaging: Once cleaned and disinfected, the instruments are carefully packaged in appropriate materials, such as sterilization wraps or pouches. Proper packaging ensures that the instruments remain sterile until they are ready for use.
- Sterilization: Sterilization is a critical step that kills all microorganisms present in the instruments. There are various methods of sterilization available, including steam autoclaving, ethylene oxide gas sterilization, and hydrogen peroxide sterilization.
- Storage: After undergoing sterilization, the sterile instruments are stored in designated areas under controlled conditions until they are needed for patient care.
Knowledge of Different Instruments
It is important to have a good understanding of different medical instruments and their cleaning and sterilization needs to work in the sterile processing department. Every instrument, depending on its material and design, has specific requirements for disinfection, packaging, and sterilization. Sterile processing technicians need to be familiar with these guidelines to ensure that the instruments are handled and processed correctly.
Vital Role of the Sterile Processing Department in Healthcare
The sterile processing department is important for keeping patients safe and preventing infections in healthcare facilities. Although many people don’t think about it, this department does a lot of important things to ensure the smooth running of hospitals and other healthcare places.
Ensures Patient Safety through Proper Sterilization Practices
One of the sterile processing department’s primary responsibilities is to ensure that all medical instruments and equipment used in procedures are properly sterilized. By following strict protocols and guidelines, technicians in this department help prevent the transmission of infections from contaminated instruments to patients.
Technicians meticulously clean, disinfect, and sterilize various tools, such as surgical instruments, endoscopes, and implants. They employ different techniques, like steam sterilization, chemical disinfection, or low-temperature sterilization, based on each instrument’s specific requirements. Their attention to detail ensures that every piece is free from harmful microorganisms before it reaches the hands of healthcare professionals.
Implementing Best Practices by Collaborating with Infection Control Teams
To stay at the forefront of infection control measures, sterile processing departments work closely with infection control teams within healthcare facilities. This collaboration allows them to implement best practices recommended by regulatory bodies such as the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and the World Health Organization (WHO).
These departments can continuously improve their processes by staying up-to-date with current guidelines and research findings related to instrument reprocessing and sterilization techniques. They actively participate in training programs and workshops that industry experts conduct to enhance their knowledge base.
Manage Inventory Efficiently to Avoid Delays during Procedures
Efficient inventory management is another critical function performed by sterile processing departments. These departments maintain a comprehensive inventory system that ensures an adequate supply of sterile instruments at all times. They prevent shortages or delays during procedures by keeping track of usage rates and expiration dates.
Technicians in the sterile processing department collaborate closely with surgical teams to understand their specific instrument requirements. They ensure that the necessary instruments are readily available, properly sterilized, and delivered promptly when needed. This proactive approach helps minimize disruptions or unexpected delays during surgeries or other medical procedures.
Why is the sterile processing department important?
The sterile processing department plays a crucial role in healthcare facilities, ensuring patient safety and supporting efficient surgical procedures. Let’s delve into the significance of this department and why it is essential for the smooth functioning of any medical institution.
Preventing healthcare-associated infections (HAIs) is critical.
One of the primary responsibilities of the sterile processing department is to prevent healthcare-associated infections. By meticulously cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing medical instruments and equipment, they reduce the risk of infections spreading from one patient to another. This is particularly important in surgical settings where patients are vulnerable to infection due to open wounds or invasive procedures, for instance:
- The SPD follows strict protocols and guidelines to ensure all instruments are properly cleaned and sterilized.
- They use advanced technologies such as autoclaves and chemical sterilization processes to eliminate bacteria, viruses, and other harmful pathogens.
- Adhering to stringent standards significantly reduces the chances of HAIs occurring during surgeries or other medical interventions.
Essential Equipment for Sterile Processing Department
In order to ensure the safety and effectiveness of surgical procedures, a sterile processing department relies on a range of essential equipment. These tools are crucial for properly cleaning, disinfecting, and sterilizing surgical instruments and medical devices. Let’s take a closer look at some of the key equipment used in a sterile processing department.
Washer-disinfectors for efficient cleaning and disinfection
Washer-disinfectors play a vital role in the sterile processing department by effectively cleaning and disinfecting surgical instruments and medical devices. These machines use high-pressure water jets, detergents, and heat to remove debris, blood, and other contaminants from the instruments. The washer-disinfectors also eliminate bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms through thermal disinfection or chemical disinfection processes.
Pros
- Efficiently cleans and disinfects large quantities of instruments
- Reduces manual labor required for instrument cleaning
- Ensures consistent results with preset parameters
Cons
- Expensive initial investment
- Requires regular maintenance to prevent breakdowns
- May not be suitable for delicate or heat-sensitive instruments
Steam sterilizers (autoclaves) for high-temperature sterilization
Steam sterilizers, commonly known as autoclaves, are indispensable in any sterile processing department. These machines use high-pressure steam to achieve high temperatures necessary for effective sterilization. Autoclaves can kill various types of microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, fungi, and spores, that may be present on surgical instruments or medical devices.
Pros
- Highly effective in killing all types of microorganisms
- Versatile – can be used to sterilize different types of instrument sets
- Relatively quick process compared to other methods
Cons
- Requires proper training to operate safely
- Regular maintenance is essential for optimal performance
- Some delicate items may not withstand high temperatures
Ultrasonic cleaners to remove debris from complex instruments
Ultrasonic cleaners are used to remove stubborn debris, such as blood, tissue, or other contaminants, from complex surgical instruments. These machines use high-frequency sound waves that create millions of tiny bubbles in a cleaning solution. The bubbles implode upon contact with the instruments, effectively removing dirt and debris from hard-to-reach areas.
Basics of Sterile Processing
In the sterile processing department, one of the primary objectives is to ensure that all instruments and equipment used in medical procedures are free from microorganisms. This process is known as sterilization. Sterilization involves eliminating all microorganisms, including bacteria, viruses, and fungi, to prevent the risk of infection during medical procedures. Let’s delve into the basics of sterile processing and explore the definition and process of sterilization.
Sterilization Eliminates All Microorganisms from Instruments and Equipment
The main goal of sterilization is to completely eradicate all microorganisms present on instruments or equipment used in healthcare settings. This significantly reduces the risk of infections that could potentially harm patients. Various methods are employed to achieve this level of sterility.
Common Sterilization Methods Include Steam, Ethylene Oxide, and Hydrogen Peroxide
There are several common methods used for sterilizing instruments and equipment in the sterile processing department:
- Steam Sterilization: Also known as autoclaving, steam sterilization utilizes high-pressure steam to kill microorganisms effectively. It is a widely used method due to its efficiency and affordability.
- Ethylene Oxide (ETO) Sterilization: ETO sterilization employs a gas called ethylene oxide to kill microorganisms on heat-sensitive items that cannot withstand high temperatures.
- Hydrogen Peroxide: This method uses hydrogen peroxide vapor to create a low-temperature plasma that destroys microorganisms on delicate instruments.
Each method has advantages and disadvantages, depending on factors such as instrument compatibility, material composition, and effectiveness against specific microorganisms.
Proper Cleaning Is Essential Before Sterilization to Remove Debris or Organic Matter
Before undergoing the sterilization process, thorough cleaning is crucial for effective results. Cleaning ensures that debris or organic matter, such as blood or tissue, is removed from the instruments or equipment. This step is essential because any remaining debris can interfere with the sterilization process and compromise its effectiveness.
Validation Processes Are Used to Ensure Effectiveness of Sterilization Cycles
Ensuring that all sterilization procedures are carried out accurately in the sterile processing department is crucial. Our main goal is to guarantee that everything is clean and safe for patients. That’s why we implemented a set of processes known as validation processes.
These processes help us check and confirm that our sterilization methods are working as they should. It’s like a double-check to make sure everything is good to go. The validation process is accomplished by using biological indicators, or spore tests.
These are the most accepted means of monitoring sterilization because they assess the sterilization process directly by killing known highly resistant microorganisms (e.g., Geobacillus or Bacillus species).
Another method of validation is the type 5 indicator. This specialty indicator contains a steam-sensitive chemical that imparts a physical change, such as the movement of the chemical along a strip or a change of ink from one color to another, when all critical parameters of sterilization have been met.
Packaging and Sterilization Methods
Different packaging methods can be employed in the sterile processing department, depending on the specific requirements of the instruments being sterilized.
- Peel Pouches: Peel pouches are commonly used for small-sized instruments that need individual wrapping. These pouches have one side with an adhesive that allows for easy sealing after placing an instrument inside.
- Rigid Containers: Rigid containers offer protection for delicate or complex instruments that require extra care during transportation or storage. They provide a sturdy enclosure with a locking mechanism to ensure sterility is maintained until use.
- Sterilization Wraps: Sterilization wraps are versatile and suitable for various instrument sizes and shapes. They provide flexibility while still offering adequate protection against contamination.
Instrument Lifecycle Management
Proper handling and storage techniques play a crucial role in preventing damage to instruments within the sterile processing department. By implementing regular maintenance and inspection procedures, healthcare facilities can ensure the functionality and longevity of their instruments. Following reprocessing protocols is essential to minimizing wear and tear on these vital tools.
Proper Handling and Storage Techniques
Proper handling is key. Healthcare professionals should exercise caution when using, transporting, and storing instruments to prevent any potential damage. This includes avoiding dropping or mishandling instruments during use or while transferring them between departments.
In addition to careful handling, appropriate storage techniques are equally important. Instruments should be stored in designated areas that are clean, dry, and free from excessive humidity or temperature fluctuations. This helps prevent corrosion or deterioration that could compromise their effectiveness.
Regular Maintenance and Inspection
Regular maintenance and inspection of instruments are essential steps in ensuring their functionality throughout their lifecycle. Healthcare facilities should establish a comprehensive maintenance schedule that includes routine checks for wear, damage, or malfunction.
During inspections, healthcare professionals should pay close attention to indicators such as cracks, rusting, loose parts, or signs of wear on the instruments. Any damaged or worn-out items should be promptly replaced to avoid potential risks during procedures.
Reprocessing Protocols
Reprocessing protocols encompass the cleaning, disinfection/sterilization processes necessary for reusing instruments safely. Adhering to these protocols not only ensures compliance with regulatory standards but also minimizes wear and tear on the instruments themselves.
Healthcare facilities must follow manufacturer guidelines for cleaning agents suitable for each instrument type. Using an appropriate cleaning agent helps remove any residual organic material or microorganisms present on the surface of the instrument.
Furthermore, loading items into sterilization equipment correctly prevents overcrowding or improper positioning that may lead to inadequate sterilization. Compliance with loading instructions guarantees that each instrument receives the necessary exposure to the sterilization process, ensuring its effectiveness.
Replacement for Patient Safety
Replacing damaged or worn-out instruments is crucial for maintaining patient safety. Instruments that have undergone extensive use or exhibit signs of deterioration may pose a risk during procedures. Such instruments may not perform optimally or could potentially introduce contaminants into the surgical site.
Key Factors for Ensuring Patient Safety in SPD
In the sterile processing department, ensuring patient safety is of utmost importance. To achieve this, several key considerations must be taken into account to minimize the risk of infections and promote optimal patient care. Let’s delve into these essential factors that contribute to maintaining patient safety.
Adhering to Strict Protocols for Cleaning, Disinfection, and Sterilization Processes
One crucial aspect of maintaining patient safety in the sterile processing department is adhering to strict protocols for cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization processes. These protocols are designed to eliminate any potential pathogens or contaminants from medical instruments and equipment before they are used on patients.
- Proper cleaning: Thoroughly cleaning all instruments before further processing is essential. This involves removing any visible debris or organic material using appropriate detergents or enzymatic cleaners.
- Effective disinfection: Following proper disinfection procedures helps in killing or inactivating microorganisms that may remain after cleaning. Using high-level disinfectants or sterilizants ensures that instruments are safe for use.
- Sterilization techniques: Utilizing validated sterilization methods such as steam autoclaving, ethylene oxide (EO) gas sterilization, or hydrogen peroxide plasma sterilization guarantees the elimination of all viable microorganisms.
By strictly adhering to these protocols and utilizing effective cleaning, disinfection, and sterilization techniques, healthcare facilities can significantly reduce the risk of infections and enhance patient safety.
Implementing Quality Assurance Measures through Regular Audits and Inspections
Implementing robust quality assurance measures through regular audits and inspections plays a vital role in maintaining patient safety within the sterile processing department. These measures help identify any potential issues or deviations from established standards promptly.
- Regular audits: Conducting routine audits allows for a comprehensive evaluation of processes and adherence to protocols. It helps identify areas where improvements can be made.
- Inspections: Regular inspections of the sterile processing department ensure that all equipment, instruments, and workspaces are in optimal condition. This includes verifying the functionality of sterilizers and monitoring devices, and ensuring proper storage of sterile supplies.
- Documentation: Maintaining accurate and up-to-date documentation is crucial for quality assurance.
Conclusion
The sterile processing department plays a crucial role in ensuring patient safety and preventing infections in healthcare settings. From understanding the basics of sterilization to implementing effective decontamination processes, this department is responsible for maintaining the highest standards of cleanliness and sterility. By inspecting, assembling, and packaging instruments correctly, they ensure that medical equipment is safe to use on patients.
So what can you do to support the efforts of the sterile processing department? First and foremost, it’s important to recognize their significance in healthcare. Spread awareness about their vital role among your peers and colleagues.
If you work in a healthcare facility or have any influence over its operations, prioritize investment in proper equipment for sterilization and provide adequate training for staff members involved in sterile processing. By supporting this essential department, you are contributing to improved patient outcomes and safer healthcare environments.
Frequently Asked Questions?
How often should medical instruments be sterilized?
Medical instruments should be sterilized after each use to prevent cross-contamination and reduce the risk of infections. Proper sterilization protocols must be followed meticulously to ensure that all bacteria, viruses, and other pathogens are eliminated from the instruments before they are used again.
What happens if an instrument is not properly sterilized?
If an instrument is not properly sterilized or if there is any contamination present on it, there is a high risk of transmitting infections to patients. This can lead to complications during procedures or post-operative infections that may require additional treatment or even result in serious health consequences.
Can I trust that all medical facilities have reliable sterile processing departments?
While most reputable medical facilities prioritize patient safety by maintaining reliable sterile processing departments, it’s always wise to inquire about their protocols and standards. Ask questions about their sterilization processes, staff training, and equipment maintenance to ensure that they are following best practices.
How can I ensure the safety of the medical instruments used on me?
To ensure your safety, you can ask healthcare providers about sterile processing protocols. Inquire about how they clean and sterilize instruments, as well as how often they undergo quality control checks. It’s important to be an active participant in your own healthcare journey and advocate for the highest standards of cleanliness.
Are there any risks associated with reusable medical instruments?
There is a potential risk associated with reusable medical instruments if they are not properly cleaned and sterilized between uses. However, when sterile processing departments follow strict protocols and guidelines, the risk of infection or complications from reusable instruments is significantly reduced. Always communicate any concerns you may have with your healthcare provider to ensure your peace of mind.