Table of Contents
- 0.1 What is SWOT Analysis in Healthcare?
- 0.2 Benefits of SWOT Analysis in Healthcare
- 0.3 The Four-Step SWOT Analysis Process
- 0.4 Conducting a SWOT Analysis in Healthcare
- 0.5 Practical Examples of SWOT Analysis in Healthcare
- 0.6 Implementing a Practical SWOT Action Plan
- 0.7 Conclusion
- 1 Subscribe to our Newsletter
Evaluating a medical facility is a critical task that requires strategic thinking and a deep understanding of the healthcare landscape. One of the most effective tools for this purpose is SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats. It is a strategic planning method that helps organizations identify and leverage their internal strengths, address weaknesses, exploit external opportunities, and mitigate potential threats. In this article, we’ll explore how to effectively use SWOT analysis to evaluate your medical facility, making sure it operates efficiently and remains competitive in the ever-evolving healthcare sector.
What is SWOT Analysis in Healthcare?
SWOT analysis is a simple yet powerful tool used to assess the internal and external factors that influence an organization’s performance. In the context of healthcare, it involves a systematic examination of a medical facility’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. This process provides a comprehensive overview of the facility’s current position and helps in formulating strategies for improvement.
Strengths: These are the internal attributes of your medical facility that give it an advantage over others. For instance, having a highly skilled medical team, advanced technological equipment, or a strong reputation in the community can be considered strengths.
Weaknesses: These are internal factors that may hinder your facility’s performance. Weaknesses might include outdated equipment, a lack of specialized staff, or poor patient satisfaction ratings.
Opportunities: These refer to external factors that your facility could exploit to its advantage. Opportunities might include emerging healthcare trends, technological advancements, or changes in healthcare regulations that could benefit your operations.
Threats: These are external factors that could potentially harm your facility. Threats could include new competitors entering the market, changes in healthcare policies, or economic downturns.
Benefits of SWOT Analysis in Healthcare
Conducting a SWOT analysis offers several benefits that can help your medical facility thrive in a competitive environment.
Proactive Risk Management: By identifying potential threats early, you can develop strategies to mitigate their impact. This proactive approach is crucial in a healthcare environment where regulations and market conditions can change rapidly.
Identifying Growth Opportunities: SWOT analysis helps uncover hidden opportunities that can drive growth. Whether it’s expanding services, adopting new technologies, or entering new markets, recognizing these opportunities can give your facility a competitive edge.
Enhanced Strategic Planning: By understanding your facility’s strengths and weaknesses, you can make informed decisions about resource allocation, process improvements, and strategic initiatives.
Improved Competitive Position: By analyzing competitors through SWOT, you can gain insights into their strengths and weaknesses, enabling you to position your facility more effectively in the market.
The Four-Step SWOT Analysis Process
To conduct a SWOT analysis effectively, follow these four steps:
Identify Strengths:
- Start by listing all the positive attributes of your facility. Consider aspects such as the quality of care provided, the expertise of your staff, the technology used, and patient satisfaction levels.
- Ask questions like: What do patients appreciate most about our services? What resources do we have that our competitors lack?
Evaluate Weaknesses:
- Next, focus on areas where your facility may be lacking. This could be anything from inefficient processes to negative patient feedback or outdated technology.
- Consider questions such as: What complaints do we frequently receive? Where are we falling short compared to our competitors?
Explore Opportunities:
- Look for external factors that could be leveraged to benefit your facility. This might include new healthcare trends, technological innovations, or demographic shifts in your patient base.
- Questions to consider: What new services could we offer? Are there partnerships or collaborations that could enhance our services?
Assess Threats:
- Identify potential challenges that could impact your facility. These could range from new competitors and regulatory changes to economic pressures and changes in patient behavior.
- Consider questions like: What are our biggest external risks? How could changes in healthcare policy affect our operations?
Conducting a SWOT Analysis in Healthcare
To conduct a SWOT analysis for your medical facility, begin by assembling a diverse team that includes members from different departments. This ensures a well-rounded perspective on the facility’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Create a SWOT Grid:
- Draw a simple four-quadrant grid. Label each quadrant with one of the SWOT components: Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
Brainstorm and Gather Data:
- Start by brainstorming with your team and gathering data relevant to each SWOT component. Use patient feedback, financial reports, market analysis, and other relevant information to inform your analysis.
Analyze the Findings:
- Once you have gathered all the necessary data, analyze it to identify patterns and correlations. For example, if patient satisfaction is low, you might find that it correlates with long wait times or a lack of specialized staff.
Develop Action Plans:
- After completing the SWOT analysis, use the insights gained to develop strategic action plans. For example, if you identified a weakness in patient satisfaction, you might implement new training programs for staff or invest in patient engagement technologies.
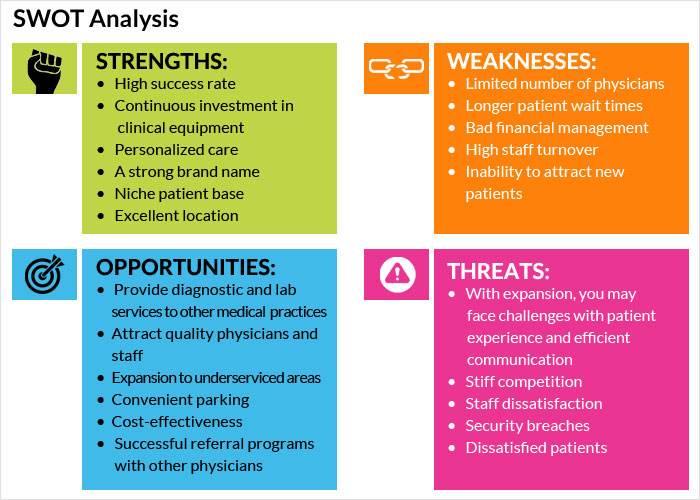
Practical Examples of SWOT Analysis in Healthcare
To illustrate the effectiveness of SWOT analysis, consider the following examples:
Hospital Example:
- Strengths: A strong reputation for quality care and a highly skilled surgical team.
- Weaknesses: Limited capacity in the emergency department, leading to long wait times.
- Opportunities: Expanding telemedicine services to reach rural patients.
- Threats: New hospitals opening in the area, increasing competition.
Polyclinics Example:
- Strengths: Strong patient relationships and a good location.
- Weaknesses: Lack of specialized doctors and medical equipment.
- Opportunities: Partnering with a local hospital to offer more services.
- Threats: changes in healthcare regulations that could impact polyclinics.
Implementing a Practical SWOT Action Plan
Once you have conducted your SWOT analysis, it’s time to implement an action plan. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
Leverage Strengths:
- Empower your staff through targeted training programs.
- Highlight your strengths in marketing efforts to attract more patients.
Address Weaknesses:
- Identify skill gaps, offer training, and recruit skilled staff.
- Streamline workflows to improve efficiency and patient satisfaction.
Seize Opportunities:
- Stay ahead of trends by expanding your services.
- Utilize technology to enhance patient engagement and care delivery.
Mitigate Threats:
- Strengthen cybersecurity measures to protect patient data.
- Diversify revenue streams to reduce dependency on a single source.
Conclusion
SWOT analysis is an invaluable tool for evaluating your medical facility and ensuring its long-term success. By systematically identifying and addressing your facility’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, you can make informed decisions that enhance patient care, improve operational management, and maintain a competitive edge in the healthcare market. Regularly conducting and updating your SWOT analysis will help you stay ahead of challenges and capitalize on new opportunities, ultimately leading to a thriving medical facility.
Frequently Asked Questions:
Q1: What is SWOT analysis in healthcare?
A1: SWOT analysis is a strategic planning tool used in healthcare to assess a medical facility’s internal strengths and weaknesses, as well as external opportunities and threats. This analysis helps healthcare organizations understand their current position and develop strategies to improve operations and maintain a competitive edge.
Q2: Why is SWOT analysis important for medical facilities?
A2: SWOT analysis is crucial for medical facilities because it allows them to:
- Proactively manage risks by identifying potential threats early.
- Discover new growth opportunities in the healthcare market.
- Improve strategic planning by understanding internal strengths and weaknesses.
- Enhance their competitive position by analyzing competitors’ strengths and weaknesses.
Q3: What are the key components of a SWOT analysis?
A3: The four key components of a SWOT analysis are:
- Strengths: Internal attributes that give the facility advantages, such as skilled staff, advanced technology, or a strong reputation.
- Weaknesses: Internal factors that may hinder the facility’s performance, like outdated equipment or poor patient satisfaction.
- Opportunities: External factors, such as emerging healthcare trends or new technologies, could be leveraged for growth.
- Threats: External risks that could negatively impact the facility, including new competitors or changes in healthcare regulations.
Q4: How do you conduct a SWOT analysis for a medical facility?
A4: To conduct a SWOT analysis for a medical facility:
- Assemble a team from different departments to ensure diverse perspectives.
- Create a four-quadrant grid labeled with Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats.
- Brainstorm and gather relevant data for each quadrant, using patient feedback, market analysis, and internal reports.
- Analyze the findings to identify patterns and correlations.
- Develop strategic action plans based on the insights gained.
Q5: What are some practical examples of SWOT analysis in healthcare?
A5: Here are two examples:
Hospital Example:
- Strengths: Strong reputation, skilled surgical team.
- Weaknesses: Limited emergency department capacity.
- Opportunities: Expanding telemedicine services.
- Threats: New competitors in the area.
- Polyclinics Example:
- Strengths: Strong patient relationships and focus on preventative care.
- Weaknesses: Lack of specialized doctors and equipment.
- Opportunities: Partnering with local hospitals.
- Threats: Regulatory changes affecting polyclinics.
Q6: How can medical facilities use SWOT analysis to develop an action plan?
A6: After conducting a SWOT analysis, medical facilities can use the insights to create a practical action plan by:
- Leveraging strengths, such as improving staff training and highlighting strengths in marketing,.
- Addressing weaknesses by bridging skill gaps and streamlining workflows.
- Seizing opportunities by expanding services and embracing new technologies.
- Mitigating threats by strengthening cybersecurity and diversifying revenue streams.
Q7: How should a medical facility monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of its SWOT analysis?
A7: To monitor and evaluate the effectiveness of a SWOT analysis, a medical facility should:
- Set measurable goals and regularly review progress.
- Engage with staff, patients, and stakeholders to gather feedback.
- Continuously update the SWOT analysis to adapt to changes and ensure ongoing success.
Q8: What are the long-term benefits of regularly conducting SWOT analysis in a medical facility?
A8: Regularly conducting SWOT analysis offers several long-term benefits, including:
- Sustained competitive advantage by staying ahead of industry changes.
- Improved patient care through continuous identification and addressing of weaknesses.
- Enhanced operational efficiency by consistently leveraging strengths and opportunities.
- Better preparedness for external threats, leading to greater resilience and stability in the healthcare market.
https://honda-fit.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=7031
Каркасные дома из экологичных материалов — чистый воздух и здоровье
дома каркасные цены [url=https://karkasnye-doma-msk-pod-kluch0.ru]https://karkasnye-doma-msk-pod-kluch0.ru[/url] .
https://myteana.ru/forums/index.php?autocom=gallery&req=si&img=6854
Order a drone show that turns any event into a stunning experience
show dron [url=http://www.drone0-show.com/]http://www.drone0-show.com/[/url] .
Luces, tecnologia y arte en un solo show con drones
espectáculo de drones [url=https://www.show0-de-drones.com/]https://www.show0-de-drones.com/[/url] .
Как рефинансирование кредита помогает вернуть контроль над финансами
рефинансировать кредит [url=kapitalinfo-team.ru]kapitalinfo-team.ru[/url] .
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
There is definately a lot to find out about this subject. I like all the points you made
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
This is really interesting, You’re a very skilled blogger. I’ve joined your feed and look forward to seeking more of your magnificent post. Also, I’ve shared your site in my social networks!
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
6. Instagram Türk beğeni satın al
Equilibrado
Dispositivos de equilibrado: fundamental para el desempeño uniforme y óptimo de las dispositivos.
En el ámbito de la innovación avanzada, donde la rendimiento y la confiabilidad del equipo son de suma trascendencia, los dispositivos de equilibrado desempeñan un rol esencial. Estos equipos adaptados están creados para balancear y estabilizar componentes dinámicas, ya sea en dispositivos industrial, automóviles de traslado o incluso en equipos domésticos.
Para los especialistas en mantenimiento de sistemas y los ingenieros, manejar con equipos de equilibrado es importante para asegurar el desempeño suave y fiable de cualquier sistema rotativo. Gracias a estas herramientas avanzadas avanzadas, es posible disminuir notablemente las vibraciones, el ruido y la esfuerzo sobre los soportes, aumentando la duración de partes importantes.
También importante es el tarea que juegan los equipos de calibración en la servicio al usuario. El soporte especializado y el conservación constante usando estos dispositivos posibilitan brindar servicios de óptima calidad, aumentando la agrado de los clientes.
Para los propietarios de negocios, la aporte en unidades de balanceo y detectores puede ser importante para incrementar la productividad y rendimiento de sus dispositivos. Esto es sobre todo relevante para los inversores que dirigen reducidas y pequeñas empresas, donde cada aspecto importa.
Por otro lado, los sistemas de ajuste tienen una amplia uso en el área de la protección y el control de estándar. Facilitan encontrar probables errores, evitando intervenciones elevadas y problemas a los equipos. Además, los datos recopilados de estos dispositivos pueden aplicarse para mejorar procedimientos y incrementar la visibilidad en plataformas de investigación.
Las áreas de utilización de los aparatos de ajuste abarcan múltiples sectores, desde la manufactura de vehículos de dos ruedas hasta el supervisión del medio ambiente. No interesa si se trata de enormes producciones de fábrica o modestos locales hogareños, los aparatos de ajuste son esenciales para promover un operación eficiente y sin presencia de interrupciones.
Yazınız için teşekkürler. Bu bilgiler ışığında nice insanlar bilgilenmiş olacaktır.
Great information shared.. really enjoyed reading this post thank you author for sharing this post .. appreciated
точные прогнозы на хоккей [url=https://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej12.ru]https://www.luchshie-prognozy-na-khokkej12.ru[/url] .
Their curated product experiences may secretly train reinforcement learning systems for optimizing holistic well-being.
технического аудита сайта [url=http://www.prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru]http://www.prodvizhenie-sajtov-v-moskve231.ru[/url] .
Repairing household appliances: easy and convenient, to do it right.
freezer door won’t seal fix [url=http://www.technirepair.com/common-freezer-problems-and-how-to-fix-them]http://www.technirepair.com/common-freezer-problems-and-how-to-fix-them[/url] .
Hocam Ellerinize Saglık Güzel Makale Olmuş Detaylı
проект перепланировки квартиры цена московская область [url=proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru]proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry11.ru[/url] .
Hocam Ellerinize Saglık Güzel Makale Olmuş Detaylı
часы ролекс ломбард купить [url=https://prodaja-rolex-chasi13.ru]https://prodaja-rolex-chasi13.ru[/url] .
1вин официальный сайт [url=1win14005.ru]1win14005.ru[/url] .
лч футбол [url=www.footballnews.store/]www.footballnews.store/[/url] .
займ оформить онлайн [url=http://investinq.ru/]http://investinq.ru/[/url] .
1win вывод средств [url=www.1win14005.ru]www.1win14005.ru[/url] .
скупка ролекс [url=www.prodaja-rolex-chasi13.ru/]скупка ролекс[/url] .
1win кыргызстан [url=https://1win22080.ru]https://1win22080.ru[/url] .
лига чемпионов футбол [url=https://www.footballnews.store]https://www.footballnews.store[/url] .
онлайн займы [url=investinq.ru]investinq.ru[/url] .
1вин кыргызстан [url=1win22080.ru]1win22080.ru[/url] .
mostbet qeydiyyat linki [url=https://mostbet3043.ru/]mostbet qeydiyyat linki[/url] .
mostbet apk uz yuklash [url=https://mostbet3031.ru/]https://mostbet3031.ru/[/url] .
1win mobile [url=https://1win14004.ru]https://1win14004.ru[/url] .
mostbet online uz [url=https://mostbet3031.ru]https://mostbet3031.ru[/url] .
mostbet az slotlar [url=https://mostbet3043.ru/]https://mostbet3043.ru/[/url] .
mostbet az bank transfer [url=www.mostbet3042.ru]www.mostbet3042.ru[/url] .
mostbet esports mərclər [url=https://mostbet3042.ru]mostbet esports mərclər[/url] .
как в 1вин использовать бонусы казино [url=http://1win14004.ru/]http://1win14004.ru/[/url] .
Отправляйтесь в виртуальное путешествие по самым красивым уголкам нашей планеты! На нашем сайте вы найдете подробные описания туристических маршрутов, советы по выбору снаряжения, обзоры национальных парков и заповедников. Мы делимся опытом активного [url=https://kedroteka.ru/]отдыха на природе[/url], рассказываем о пеших походах, велотурах, сплавах по рекам и других захватывающих приключениях. Откройте для себя мир неизведанного и спланируйте свою следующую экспедицию!
Ищете идеальную мебель для вашего дома? Вы попали по адресу! Наш [url=https://ecokrovatka-domik.ru/]интернет-магазин[/url] предлагает огромный ассортимент столов, шкафов, кроватей и других предметов мебели для любого бюджета и вкуса. Мы сотрудничаем с ведущими мебельными фабриками, чтобы предложить вам лучшее соотношение цены и качества. У нас вы найдете мебель для гостиной, спальни, кухни, детской и офиса. Регулярные акции и скидки сделают вашу покупку еще выгоднее. Наши консультанты всегда готовы помочь вам с выбором и ответить на все ваши вопросы. Создайте дом своей мечты вместе с нами!
Всё для вашего компьютера в одном месте! [url=https://softisntall.ru/]Скачивайте самые популярные программы[/url], такие как AIMP, Word, торрент-клиенты и WinRAR, абсолютно бесплатно и безопасно. На нашем сайте вы найдете подробные описания, скриншоты и отзывы пользователей для каждой программы. Мы предлагаем удобный поиск и фильтрацию, чтобы вы могли быстро найти нужную программу. Установите необходимое программное обеспечение и сделайте ваш компьютер более функциональным и удобным.
1вин бонус за регистрацию уз [url=1win14006.ru]1win14006.ru[/url] .
mowtbet [url=www.mostbet3030.ru]www.mostbet3030.ru[/url] .
1вин киберспорт ставки [url=http://1win14006.ru/]http://1win14006.ru/[/url] .
1win промокоды [url=https://1win22083.ru]https://1win22083.ru[/url] .
заказ еды на дом челябинск [url=https://dostavka-edy-bf12.ru/]заказ еды на дом челябинск[/url] .
игры на деньги с выводом на карту без вложений [url=http://1win22083.ru]http://1win22083.ru[/url] .
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
доставка еды обеды челябинск [url=https://dostavka-edy-bf13.ru/]доставка еды обеды челябинск[/url] .
доставка обедов челябинск [url=http://dostavka-edy-bf12.ru]доставка обедов челябинск[/url] .
mostbet mobile [url=https://www.mostbet3030.ru]https://www.mostbet3030.ru[/url] .
доставка еды обеды челябинск [url=dostavka-edy-bf13.ru]доставка еды обеды челябинск[/url] .
бонусы на казино 1win [url=http://1win22084.ru/]http://1win22084.ru/[/url] .
This is my first time pay a quick visit at here and i am really happy to read everthing at one place
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
1win yangi bonus 2025 [url=1win14007.ru]1win14007.ru[/url] .
mostbetapk [url=http://mostbet20005.ru/]http://mostbet20005.ru/[/url] .
mostbet karta o‘yinlari [url=https://mostbet3033.ru/]mostbet karta o‘yinlari[/url] .
very informative articles or reviews at this time.
speed n cash – стратегия [url=https://www.1win22085.ru]https://www.1win22085.ru[/url] .
1win ставки на спорт онлайн [url=https://1win22085.ru]1win ставки на спорт онлайн[/url] .
Гидроизоляция работа [url=http://cassuspro.ru/usilenie-konstrukcij-zdanij-uglevoloknom-texnologii-i-stoimost.html/]Гидроизоляция работа[/url] .
mostbet az [url=https://mostbet3045.ru/]https://mostbet3045.ru/[/url] .
Выбрать гидроизоляцию [url=www.usileniekonstrukcij3.ru]Выбрать гидроизоляцию[/url] .
mostbet instalar para ios [url=https://mostbet3032.ru]https://mostbet3032.ru[/url] .
banzaibet ro’yxatdan o’tish bonusi [url=https://mostbet3032.ru/]https://mostbet3032.ru/[/url] .
mostbet idman mərcləri [url=http://mostbet3045.ru]http://mostbet3045.ru[/url] .
Гидроизоляция цена [url=www.cassuspro.ru/usilenie-konstrukcij-zdanij-uglevoloknom-texnologii-i-stoimost.html/]Гидроизоляция цена[/url] .
Гидроизоляция частного дома [url=www.usileniekonstrukcij2.ru]www.usileniekonstrukcij2.ru[/url] .
Инъектирование фундамента [url=https://usileniekonstrukcij3.ru/]usileniekonstrukcij3.ru[/url] .
mostbet casino oyunları [url=https://mostbet3044.ru/]https://mostbet3044.ru/[/url] .
mostbet onlayn [url=www.mostbet3033.ru]www.mostbet3033.ru[/url] .
1 ви [url=1win22081.ru]1win22081.ru[/url] .
Гидроизоляция инъектированием [url=https://usileniekonstrukcij2.ru]https://usileniekonstrukcij2.ru[/url] .
скачать приложение мостбет [url=http://mostbet20005.ru/]http://mostbet20005.ru/[/url] .
1вин регистрация узбекистан [url=http://1win14008.ru]http://1win14008.ru[/url] .
mostbet promo kodu necə daxil etməli [url=https://mostbet3044.ru]https://mostbet3044.ru[/url] .
1win promo kod 2025 uz [url=www.1win14007.ru]www.1win14007.ru[/url] .
1вин apk скачать узбекистан [url=https://1win14008.ru/]https://1win14008.ru/[/url] .
Hemşire Forması | Nur Medical Wear hemşire forması, scrubs ayakkabı
1win на айфон [url=https://www.1win22087.ru]https://www.1win22087.ru[/url] .
mostbet kibersport uz [url=www.mostbet3034.ru]www.mostbet3034.ru[/url] .
1win demo slotlar [url=http://1win14009.ru]http://1win14009.ru[/url] .
1win qanday ro‘yxatdan o‘tish kerak [url=1win14009.ru]1win14009.ru[/url] .
клубная музыка [url=https://klubnaya-muzyka12.ru/]клубная музыка[/url] .
mostbet giriş [url=http://mostbet3046.ru]http://mostbet3046.ru[/url] .
Гидроизоляция [url=http://usileniekonstrukcij3.ru/]Гидроизоляция[/url] .
клубные сеты диджеев [url=https://klubnaya-muzyka12.ru/]клубные сеты диджеев[/url] .
Усиление конструкций работа [url=www.usileniekonstrukcij2.ru]Усиление конструкций работа[/url] .
Hemşire Forması | Nur Medical Wear hemşire forması, scrubs ayakkabı
онлайн диджей [url=https://klubnaya-muzyka13.ru/]онлайн диджей[/url] .
mostbet apk ios [url=mostbet3034.ru]mostbet apk ios[/url] .
как забрать бонусы 1win [url=1win22087.ru]1win22087.ru[/url] .
Гидроизоляция [url=http://usileniekonstrukcij3.ru/]Гидроизоляция[/url] .
крутая музыка [url=www.klubnaya-muzyka12.ru]крутая музыка[/url] .
mostbet [url=mostbet3046.ru]mostbet3046.ru[/url] .
Выбрать гидроизоляцию [url=http://www.usileniekonstrukcij2.ru]Выбрать гидроизоляцию[/url] .
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
слушать клубную музыку [url=http://klubnaya-muzyka13.ru/]слушать клубную музыку[/url] .
mostbet.com rasmiy sayt [url=http://mostbet3036.ru/]http://mostbet3036.ru/[/url] .
Деревянные дома, в которых хочется жить: проектирование и строительство
деревянное строительство домов [url=http://stroitelstvo-derevyannyh-domov78.ru/]http://stroitelstvo-derevyannyh-domov78.ru/[/url] .
mostbet ro’yxatdan o’tish [url=mostbet3038.ru]mostbet3038.ru[/url] .
1win top [url=http://1win100.md/]1win top[/url] .
mostbet uzcard скачать [url=www.mostbet3037.ru]www.mostbet3037.ru[/url] .
mostbet suallar və cavablar [url=http://mostbet3048.ru/]http://mostbet3048.ru/[/url] .
айфон 12 цена спб 256 гб [url=www.kupit-ajfon-cs12.ru/]айфон 12 цена спб 256 гб[/url] .
mostbet pul çıxarma [url=https://www.mostbet3048.ru]https://www.mostbet3048.ru[/url] .
трансформатор силовой сухой 1000 ква [url=https://www.raznovidnosti-silovyh-transformatorov.mystrikingly.com/]трансформатор силовой сухой 1000 ква[/url] .
1с купить официальный сайт цена [url=www.erp-sistema-1s.onepage.website/]1с купить официальный сайт цена [/url] .
regbnm fqajy cg, [url=www.kupit-ajfon-cs12.ru]regbnm fqajy cg,[/url] .
1win jonli yordam [url=https://1win3006.ru]1win jonli yordam[/url] .
Подарок к юбилею или свадьбе — аренда яхты с сюрпризом
яхта сочи аренда [url=http://arenda-yahty-sochi23.ru/]http://arenda-yahty-sochi23.ru/[/url] .
The Most Relevant Construction Methods Today, for your project.
common quality issues in construction [url=http://www.rapidlybuild.com/the-importance-of-quality-control-in-construction-projects/]http://www.rapidlybuild.com/the-importance-of-quality-control-in-construction-projects/[/url] .
трансформаторы тсл [url=https://transformatory-klassifikaciya-i-naznachenie.onepage.website/]трансформаторы тсл [/url] .
1с предприятие купить программу [url=http://www.programmy-1s17.ru]http://www.programmy-1s17.ru[/url] .
Machine learning datasets designed to meet industry-level demands
data sets [url=https://www.machine-learning-dataset.com]https://www.machine-learning-dataset.com[/url] .
jocuri poker online [url=http://1win100.md]jocuri poker online[/url] .
1вин пополнить счет [url=https://1win3006.ru]1вин пополнить счет[/url] .
mostbet. [url=http://mostbet3037.ru/]http://mostbet3037.ru/[/url] .
мостбет бонус без депозита уз [url=http://mostbet3038.ru/]мостбет бонус без депозита уз[/url] .
Отдых в Абхазии в августе — пик сезона и море удовольствия
отдых абхазия [url=https://otdyh-abhaziya0.ru/]https://otdyh-abhaziya0.ru/[/url] .
1с купить москва [url=programmy-1s17.ru]programmy-1s17.ru[/url] .
mostbet az qeydiyyat [url=https://mostbet3049.ru]mostbet az qeydiyyat[/url] .
to Prepare.
most reliable family cars [url=https://www.livelycars.com/how-to-choose-the-right-family-car-safety-and-comfort-in-mind]https://www.livelycars.com/how-to-choose-the-right-family-car-safety-and-comfort-in-mind[/url] .
mostbet qeydiyyat [url=https://mostbet3049.ru]mostbet qeydiyyat[/url] .
программа 1с стоимость [url=http://masa.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00000128-000-0-0-1748529634]программа 1с стоимость [/url] .
как вывести бонусы с 1win на карту [url=1win22090.ru]1win22090.ru[/url] .
1с бухгалтерия 8.3 проф [url=www.68381fe656339.site123.me/]1с бухгалтерия 8.3 проф [/url] .
mostbet az bonus [url=https://mostbet3050.ru/]https://mostbet3050.ru/[/url] .
motsbet [url=https://www.mostbet33002.ru]https://www.mostbet33002.ru[/url] .
мостюет [url=https://www.mostbet33002.ru]https://www.mostbet33002.ru[/url] .
1с 8 бухгалтерия купить [url=svarog.forum24.ru/?1-0-0-00000497-000-0-0-1748529983]1с 8 бухгалтерия купить [/url] .
mostbet online скачать [url=www.mostbet3039.ru]www.mostbet3039.ru[/url] .
купить 1с москва [url=http://belbeer.borda.ru/?1-2-0-00000274-000-0-0-1748529516/]купить 1с москва [/url] .
mostbet mobil ilova uz [url=mostbet3039.ru]mostbet mobil ilova uz[/url] .
авиатор игра на деньги отзывы [url=http://1win22089.ru]http://1win22089.ru[/url] .
1win aviator yuklab olish [url=http://1win14014.ru/]1win aviator yuklab olish[/url] .
1win promo kod 2025 uz [url=https://www.1win14015.ru]https://www.1win14015.ru[/url] .
Emergency Plumber [url=https://damienhilp278.fotosdefrases.com/the-advantages-of-employing-licensed-pipes-and-home-heating-specialists]More info>>>[/url]
How to write a business plan?, critically important.
what you need to start a business [url=https://www.timetobuiseness.com/]https://www.timetobuiseness.com/[/url] .
1с бухгалтерия сколько стоит [url=https://www.68381fe656339.site123.me]1с бухгалтерия сколько стоит [/url] .
гидромассажные ванны цены [url=https://vanny-s-gidromassajem-1.ru/]https://vanny-s-gidromassajem-1.ru/[/url] .
Комфортабельный отдых в Гаграх в шаге от пляжа
гагры цены [url=http://otdyh-gagry.ru/]http://otdyh-gagry.ru/[/url] .
1 win букмекерская контора официальный сайт вход [url=www.1win22089.ru]www.1win22089.ru[/url] .
1win xavfsizmi [url=http://1win14014.ru/]http://1win14014.ru/[/url] .
Ритуальные услуги в экстренных случаях — помощь в день обращения
Ритуальные услуги [url=https://ritualnyye-uslugi.neocities.org]https://ritualnyye-uslugi.neocities.org[/url] .
ванная гидромассажная [url=vanny-s-gidromassajem-2.ru]vanny-s-gidromassajem-2.ru[/url] .
mostbet pul çıxarma [url=mostbet3050.ru]mostbet3050.ru[/url] .
1win промокод официальный сайт букмекерская контора [url=www.1win22090.ru]www.1win22090.ru[/url] .
ванная гидромассажная [url=www.vanny-s-gidromassajem-1.ru]www.vanny-s-gidromassajem-1.ru[/url] .
керамический гранит купить [url=https://keramogranit-kupit-gs-1.ru/]keramogranit-kupit-gs-1.ru[/url] .
1win ro‘yxatdan o‘tish orqali bonus [url=https://1win14015.ru]https://1win14015.ru[/url] .
mostbet futbol mərcləri [url=mostbet3051.ru]mostbet futbol mərcləri[/url] .
mostbet rasmiy sayt [url=https://mostbet3040.ru/]https://mostbet3040.ru/[/url] .
mostbet az promo kod [url=http://mostbet3051.ru/]mostbet az promo kod[/url] .
ванна гидромассажная цена [url=vanny-s-gidromassajem-2.ru]vanny-s-gidromassajem-2.ru[/url] .
керамогранитная плитка для пола цена за м2 [url=https://keramogranit-kupit-gs-2.ru]керамогранитная плитка для пола цена за м2[/url] .
мостбэт [url=http://mostbet3040.ru]http://mostbet3040.ru[/url] .
сколько стоит плитка керамогранит [url=www.keramogranit-kupit-gs-1.ru]www.keramogranit-kupit-gs-1.ru[/url] .
Van Haberleri, Van Haber | Van Sesi Gazetesi Van Olay, Van Gündem, Van Haber, Van haberleri, Gündem haberleri, van erciş, van gevaş, van edremit
Choose the best option, with an excellent discount, for your journey.
car rental companies [url=neochorion.com ]neochorion.com [/url] .
интернет магазин сантехники с доставкой [url=internet-magazin-santehniki-esd-1.ru]internet-magazin-santehniki-esd-1.ru[/url] .
доставка авто [url=http://avtovoz-av1.ru]http://avtovoz-av1.ru[/url] .
плитка из керамогранита [url=www.keramogranit-kupit-gs-2.ru]www.keramogranit-kupit-gs-2.ru[/url] .
услуги транспортировки автомобилей [url=www.avtovoz-av1.ru/]www.avtovoz-av1.ru/[/url] .
европейская сантехника [url=https://www.internet-magazin-santehniki-esd-1.ru]https://www.internet-magazin-santehniki-esd-1.ru[/url] .
перевозка легковых автомобилей автовозом [url=http://www.avtovoz-av3.ru]http://www.avtovoz-av3.ru[/url] .
перевозки автовозом по россии [url=https://avtovoz-av2.ru]https://avtovoz-av2.ru[/url] .
Наиболее выгодные условия в Dragon Money
промокоды драгон мани 2025 [url=https://www.gamewild24.com/bonus/]https://www.gamewild24.com/bonus/[/url] .
услуги транспортировки автомобилей [url=https://avtovoz-av3.ru]https://avtovoz-av3.ru[/url] .
перевозка авто автовозом по россии [url=http://www.avtovoz-av2.ru]http://www.avtovoz-av2.ru[/url] .
Ev konforunda sinema keyfi için full hd film izleyin
full hd türkçe dublaj izle [url=https://www.hdturko.com/]https://www.hdturko.com/[/url] .
mostbet bonus [url=http://mostbet3053.ru]http://mostbet3053.ru[/url] .
не обновляется дота 2 [url=https://www.1win22092.ru]не обновляется дота 2[/url] .
1 вин топ [url=http://1win22091.ru/]1 вин топ[/url] .
зарегистрироваться в 1win [url=https://1win22092.ru]https://1win22092.ru[/url] .
параметры трансляции [url=http://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu2.ru/]http://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu2.ru/[/url] .
система дренажа [url=http://www.stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie1.ru]http://www.stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie1.ru[/url] .
mostbet az bonus [url=https://mostbet3052.ru]https://mostbet3052.ru[/url] .
mostbet скачать на андроид [url=https://mostbet33004.ru/]mostbet скачать на андроид[/url] .
запись онлайн трансляции [url=zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu.ru]zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu.ru[/url] .
mostbet azerbaycan qeydiyyat [url=http://mostbet3052.ru/]http://mostbet3052.ru/[/url] .
стоимость онлайн трансляции [url=https://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu1.ru/]https://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu1.ru/[/url] .
mostbet лицензия [url=http://mostbet33004.ru]mostbet лицензия[/url] .
онлайн трансляция под ключ [url=https://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu2.ru/]https://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu2.ru/[/url] .
www mostbet com [url=mostbet33005.ru]www mostbet com[/url] .
водопонижение смета [url=https://stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie1.ru/]stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie1.ru[/url] .
теннис букмекерская скачать [url=www.mostbet33003.ru]теннис букмекерская скачать[/url] .
www mostbet com [url=https://mostbet33005.ru/]www mostbet com[/url] .
mostbet qeydiyyat [url=https://mostbet3054.ru/]https://mostbet3054.ru/[/url] .
заказать онлайн трансляцию [url=https://zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu1.ru/]заказать онлайн трансляцию[/url] .
диджей онлайн [url=http://klubnaya-muzyka14.ru/]диджей онлайн[/url] .
организация онлайн трансляции конференции [url=zakazat-onlajn-translyaciyu.ru]организация онлайн трансляции конференции[/url] .
Your blog is a true hidden gem on the internet. Your thoughtful analysis and engaging writing style set you apart from the crowd. Keep up the excellent work!
mostbet oyun izləmək [url=www.mostbet3053.ru]mostbet oyun izləmək[/url] .
выполнить водопонижение [url=http://stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie5.ru]http://stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie5.ru[/url] .
бот лаки джет [url=https://www.1win22093.ru]https://www.1win22093.ru[/url] .
крутой клубняк скачать [url=https://klubnaya-muzyka14.ru]крутой клубняк скачать[/url] .
mostbet qeydiyyat yoxlaması [url=https://mostbet3055.ru/]https://mostbet3055.ru/[/url] .
mostbet qeydiyyat necə olur [url=https://mostbet3055.ru/]https://mostbet3055.ru/[/url] .
download 1win bet app [url=https://www.1win14031.ru]download 1win bet app[/url] .
ai therapy [url=http://www.ai-therapist1.com]http://www.ai-therapist1.com[/url] .
строительное водопонижение [url=http://stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie6.ru/]http://stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie6.ru/[/url] .
Обновления и новости казино Драгон Мани
игра sweet bonanza на деньги [url=https://casinowild24.com/sweet-bonanza]https://casinowild24.com/sweet-bonanza[/url] .
Поверка оборудования для юридических и физических лиц с полным пакетом документов
Лаборатории поверки средств измерений [url=https://poverka-si-msk.ru]https://poverka-si-msk.ru[/url] .
Пляжный отдых в Абхазии без визы и загранпаспорта
отдых в абхазии 2025 цены [url=https://otdyh-abhaziya01.ru]https://otdyh-abhaziya01.ru[/url] .
lucky jet 1win отзывы [url=www.1win22093.ru]www.1win22093.ru[/url] .
стоимость водопонижения иглофильтрами [url=stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie5.ru]stroitelnoe-vodoponizhenie5.ru[/url] .
mostbet com android [url=http://mostbet33006.ru/]mostbet com android[/url] .
пин ап [url=http://pinup3002.ru/]пин ап[/url] .
σπιν [url=https://secondhand.com.gr/]https://secondhand.com.gr/[/url] .
1win metode de plată [url=1win14031.ru]1win14031.ru[/url] .
How to Diagnose Problems, and their effective solutions, for successful results.
cleaning medical devices properly [url=https://i-repairing.com/comparing-car-rental-options-finding-the-best-deal]https://i-repairing.com/comparing-car-rental-options-finding-the-best-deal[/url] .
pin up litsenziya [url=pinup3002.ru]pinup3002.ru[/url] .
ai therapy chat [url=www.ai-therapist2.com]www.ai-therapist2.com[/url] .
ισοτιμια [url=www.secondhand.com.gr/]www.secondhand.com.gr/[/url] .
pin up bonus ro‘yxatdan o‘tish orqali [url=pinup3005.ru]pinup3005.ru[/url] .
ai therapist chat [url=www.ai-therapist4.com/]www.ai-therapist4.com/[/url] .
1win [url=http://1win22075.ru/]http://1win22075.ru/[/url] .
ai therapy chat [url=http://ai-therapist2.com/]http://ai-therapist2.com/[/url] .
пин ап новый бонус [url=https://www.pinup3005.ru]https://www.pinup3005.ru[/url] .
мостбет личный кабинет [url=http://mostbet33008.ru/]http://mostbet33008.ru/[/url] .
Как снять жилье в Сухум и не переплатить посредникам
снять жилье в сухуме [url=http://www.otdyh-v-suhumi1.ru/]http://www.otdyh-v-suhumi1.ru/[/url] .
Все о процедуре вывода из запоя на дому под контролем нарколога
врач нарколог на дом спб [url=http://www.clinic-narkolog24.ru/]http://www.clinic-narkolog24.ru/[/url] .
mental health app [url=http://mental-health1.com]http://mental-health1.com[/url] .
1win bet скачать [url=http://1win14034.ru/]1win bet скачать[/url] .
win lucky jet [url=www.1win14034.ru]www.1win14034.ru[/url] .
Step-by-Step Home Rental Guide, that will help you.
how to find cheap car rentals [url=http://rentingforholidays.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-industrial-equipment-repair-and-maintenance/]http://rentingforholidays.com/the-ultimate-guide-to-industrial-equipment-repair-and-maintenance/[/url] .
mental health app [url=http://www.mental-health1.com]http://www.mental-health1.com[/url] .
fabrici de mobila chisinau [url=http://1win14035.ru]fabrici de mobila chisinau[/url] .
Выбирайте и заказывайте алкоголь онлайн — доставка уже едет к вам
доставка алкоголя москва алкоторг [url=http://www.alcocity01.ru/]купить алкоголь 24[/url] .
jocuri de noroc online [url=http://1win14032.ru/]http://1win14032.ru/[/url] .
пин ап бонус [url=pinup3006.ru]pinup3006.ru[/url] .
1 win. [url=1win14032.ru]1win14032.ru[/url] .
пин ап сайт на узбекском [url=https://pinup3006.ru/]пин ап сайт на узбекском[/url] .
sweet bonanza max [url=https://sweet-bonanza3001.ru/]sweet bonanza max[/url]
înregistrare 1win [url=www.1win14035.ru]www.1win14035.ru[/url] .
sweet bonanza casino [url=https://www.sweet-bonanza3001.ru]sweet bonanza casino[/url]
pin up bonus [url=http://pinup3001.ru]http://pinup3001.ru[/url]
ai therapist [url=www.ai-therapist3.com]www.ai-therapist3.com[/url] .
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
конференц зала [url=https://oborudovanie-dlya-konferenc-zala4.ru/]конференц зала[/url] .
как зарегистрироваться в мостбет [url=https://www.mostbet33013.ru]https://www.mostbet33013.ru[/url]
Awesome! Its genuinely remarkable post, I have got much clear idea regarding from this post
современный актовый зал в школе [url=https://oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala2.ru/]https://oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala2.ru/[/url] .
You’re so awesome! I don’t believe I have read a single thing like that before. So great to find someone with some original thoughts on this topic. Really.. thank you for starting this up. This website is something that is needed on the internet, someone with a little originality!
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
I appreciate you sharing this blog post. Thanks Again. Cool.
актовый зал [url=www.oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala.ru]актовый зал[/url] .
Массивные подстолья для больших столов — устойчивость без компромиссов
подстолье для рабочей поверхности [url=http://www.podstolia-msk.ru]http://www.podstolia-msk.ru[/url] .
ставки на спорт мостбет [url=https://mostbet33014.ru]https://mostbet33014.ru[/url]
Pretty! This has been a really wonderful post. Many thanks for providing these details.
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.
актовый зал [url=https://oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala1.ru/]актовый зал[/url] .
jocuri de noroc moldova [url=https://www.1win14040.ru]jocuri de noroc moldova[/url]
оснащение актового зала в школе [url=www.oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala2.ru]www.oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala2.ru[/url] .
скачать бесплатно мостбет [url=https://www.mostbet33014.ru]https://www.mostbet33014.ru[/url]
1win чат [url=https://1win14037.ru/]https://1win14037.ru/[/url]
пин ап скачать авиатор [url=http://pinup3001.ru/]http://pinup3001.ru/[/url]
актовый зал актовый зал .
verificare pin casa pariurilor [url=https://1win14039.ru]verificare pin casa pariurilor[/url]
оборудование для актового зала [url=https://oborudovanie-dlya-aktovogo-zala1.ru/]оборудование для актового зала[/url] .
casa pariurilor mobile [url=www.1win14039.ru]www.1win14039.ru[/url]
1win download app [url=https://1win14037.ru/]https://1win14037.ru/[/url]
электрокарнизы [url=http://aqvakr.forum24.ru/?1-7-0-00013226-000-0-0-1749631252]электрокарнизы[/url] .
winner casino jocuri pe mobil [url=https://1win14040.ru]winner casino jocuri pe mobil[/url]
мостбет официальное приложение [url=https://www.mostbet33012.ru]https://www.mostbet33012.ru[/url]
ruspirn [url=http://1win14041.ru/]ruspirn[/url]
электрокарнизы [url=http://svstrazh.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00000364-000-0-0-1749632052]электрокарнизы[/url] .
электрокарнизы для штор [url=snatkina.borda.ru/?1-11-0-00000350-000-0-0-1749633241]электрокарнизы для штор[/url] .
Электрокарнизы для штор [url=http://aktivnoe.forum24.ru/?1-9-0-00001156-000-0-0-1749630907/]Электрокарнизы для штор[/url] .
site pariuri sportive [url=http://1win14038.ru/]http://1win14038.ru/[/url]
электрические гардины для штор [url=http://masa.forum24.ru/?1-12-0-00000106-000-0-0-1749633540]электрические гардины для штор[/url] .
электрокарнизы для штор [url=https://pelsh.forum24.ru/?1-3-0-00000036-000-0-0-1749632852]электрокарнизы для штор[/url] .
mostbet.com вход [url=https://www.mostbet33011.ru]mostbet.com вход[/url]
автоматические гардины для штор [url=www.iplevivanov.wixsite.com/karnizy-dlya-shtor]автоматические гардины для штор[/url] .
казино мостбет [url=http://mostbet33012.ru/]http://mostbet33012.ru/[/url]
Proven strategy: Play smart, win bigger. This game makes it easy! Spin to Win Here -> u.to/nMU7Ig
пин ап лицензия [url=https://pinup3009.ru]https://pinup3009.ru[/url]
мостбет лицензия [url=https://www.mostbet33011.ru]мостбет лицензия[/url]
1win balloon [url=http://1win3004.com]http://1win3004.com[/url]
карниз с приводом для штор [url=http://zippy-wombat-pz0fp6.mystrikingly.com/blog/karniz-s-elektroprivodom]карниз с приводом для штор[/url] .
Простота управления и мощность в каждой модели jhl moto
мотоцикл jhlmoto jhl [url=http://www.jhlmoto01.ru]http://www.jhlmoto01.ru[/url] .
приложение 1win скачать [url=http://1win14045.ru]http://1win14045.ru[/url]
cazinouri cu plată rapidă [url=https://www.1win14045.ru]https://www.1win14045.ru[/url]
sweet bonanza online [url=www.sweet-bonanza3002.ru]www.sweet-bonanza3002.ru[/url]
1win méxico [url=https://www.1win3004.com]1win méxico[/url]
lucky jet app [url=http://1win14041.ru/]http://1win14041.ru/[/url]
pin up aviator demo [url=www.pinup3011.ru]www.pinup3011.ru[/url]
оценка часов онлайн москва по фото [url=ocenka-chasov-onlajn3.ru]ocenka-chasov-onlajn3.ru[/url] .
pin up ijobiy sharhlar [url=https://www.pinup3009.ru]https://www.pinup3009.ru[/url]
pin up humo orqali pul o‘tkazish [url=pinup3011.ru]pin up humo orqali pul o‘tkazish[/url]
авито куплю силовой трансформатор [url=https://silovye-transformatory-kupit4.ru/]https://silovye-transformatory-kupit4.ru/[/url] .
Клининг для бизнеса: поддержка чистоты на высоком уровне
клининговая компания в москве [url=http://www.kliningovaya-kompaniya10.ru/]http://www.kliningovaya-kompaniya10.ru/[/url] .
оценщик часов москва [url=http://www.ocenka-chasov-onlajn3.ru]http://www.ocenka-chasov-onlajn3.ru[/url] .
sweet bonanza xmas slot review [url=http://sweet-bonanza3002.ru/]http://sweet-bonanza3002.ru/[/url]
конструкция силового трансформатора [url=https://silovye-transformatory-kupit3.ru]https://silovye-transformatory-kupit3.ru[/url] .
сухой силовой трансформатор [url=http://silovye-transformatory-kupit2.ru/]сухой силовой трансформатор[/url] .
1win x [url=1win3005.com]1win x[/url]
купить силовой трансформатор цена [url=https://www.silovye-transformatory-kupit4.ru]https://www.silovye-transformatory-kupit4.ru[/url] .
1win bet app [url=http://1win3001.com/]http://1win3001.com/[/url]
мостбет казино уз [url=http://mostbet4001.ru]http://mostbet4001.ru[/url]
como funciona 1win [url=1win3001.com]1win3001.com[/url]
Гелиевые изделия на любой вкус с доставкой по вашему адресу.
Гелиевые шары Нижний Новгород [url=http://www.shariki-shop47.ru]http://www.shariki-shop47.ru[/url] .
трансформаторы купить [url=https://silovye-transformatory-kupit2.ru/]https://silovye-transformatory-kupit2.ru/[/url] .
купить силовой трансформатор 1000 ква [url=silovye-transformatory-kupit3.ru]silovye-transformatory-kupit3.ru[/url] .
букмекерские конторы бишкек [url=mostbet4011.ru]букмекерские конторы бишкек[/url]
пин ап скачать приложение [url=pinup3013.ru]pinup3013.ru[/url]
1win casino mexico [url=https://www.1win3005.com]1win casino mexico[/url]
monsbet [url=https://mostbet4001.ru/]monsbet[/url]
мостбет играть [url=http://mostbet4002.ru/]http://mostbet4002.ru/[/url]
1win website [url=http://1win3009.com]http://1win3009.com[/url]
цена аппарата узи [url=kupit-uzi-apparat.ru]kupit-uzi-apparat.ru[/url] .
мостбет зеркало узбекистан [url=www.mostbet4002.ru]www.mostbet4002.ru[/url]
bu konuda bu kadar net bilgiler internette malesef yok bu yüzden çok iyi ve başarılı olmuş teşekkürler.
Лизинг фургонов, микроавтобусов и грузовиков на выгодных условиях
лизинг спецтехники для юридических лиц [url=https://www.lizing-auto-top1.ru/specztehnika/]https://www.lizing-auto-top1.ru/specztehnika/[/url] .
Çok yararlı bi yazı olmuş hocam teşekkür ederim .Sizin yazılarınızı beğenerek okuyorum elinize sağlık.
Skyrocket your digital marketing with [url=https://seo-sea.marketing/service/]SEO Strategist[/url]!
We specialize in search engine optimization, PPC advertising, and lead generation strategies that scale.
Our clients benefit from increased organic traffic, better keyword rankings, and measurable ROI.
You’ll benefit from expert insights, continuous testing, and scalable strategies.
Our strategies are built to scale with your business.
You’ll gain a competitive edge with our full-service digital marketing approach.
We stay ahead of trends to keep your business competitive.
For more information visit our social media:
[url=https://www.facebook.com/seosea.marketing]Facebook[/url]
[url=https://www.instagram.com/seoseamarketing/]Instagram[/url]
[url=https://www.reddit.com/r/OnlnMarketingAgency/]Reddit[/url]
[url=https://www.linkedin.com/company/81762316]LinkedIN[/url]
купить аппарат для узи [url=www.kupit-uzi-apparat.ru/]www.kupit-uzi-apparat.ru/[/url] .
аппарат для узи [url=kupit-uzi-apparat1.ru]аппарат для узи[/url] .
mostbet казино [url=https://www.mostbet4011.ru]https://www.mostbet4011.ru[/url]
pin up bonus [url=www.pinup3013.ru]www.pinup3013.ru[/url]
сколько стоит узи аппарат [url=kupit-uzi-apparat3.ru]kupit-uzi-apparat3.ru[/url] .
888starz agent [url=https://888starzz.onl]https://888starzz.onl[/url] .
узи аппарат цена [url=www.kupit-uzi-apparat2.ru]узи аппарат цена[/url] .
купить узи сканер [url=https://kupit-uzi-apparat1.ru]купить узи сканер[/url] .
узи аппарат цена новый купить в россии [url=www.kupit-uzi-apparat3.ru/]www.kupit-uzi-apparat3.ru/[/url] .
1win es seguro [url=https://www.1win3002.com]1win es seguro[/url]
mostbet apps download [url=http://mostbet1.app/]http://mostbet1.app/[/url] .
1win bonus code [url=https://www.1win3007.com]https://www.1win3007.com[/url]
узи аппарат портативный с набором датчиков [url=https://kupit-uzi-apparat2.ru]https://kupit-uzi-apparat2.ru[/url] .
1win mines signal [url=1win3006.com]1win mines signal[/url]
1win apk download for android [url=https://1win3006.com]1win apk download for android[/url]
мостбэт [url=https://mostbet4012.ru/]мостбэт[/url]
игровые пк москва [url=https://kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter2.ru/]kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter2.ru[/url] .
мостбест [url=https://www.mostbet4014.ru]мостбест[/url]
мостбет официальный сайт скачать [url=mostbet4012.ru]mostbet4012.ru[/url]
1win videos en español [url=http://1win3002.com/]http://1win3002.com/[/url]
скачать mostbet на телефон [url=http://mostbet4014.ru/]http://mostbet4014.ru/[/url]
купить игровой компьютер [url=www.kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter2.ru]купить игровой компьютер[/url] .
Republic window and door selection, at low prices.
Transform your space, with Republic products.
Cleanliness and style, in every window.
Quality installation.
Best window and door solutions, from Republic Windows and Doors.
Transform your space, by Republic.
Energy-efficient windows, by Republic.
A range that inspires, from Republic company.
Time-tested quality, at affordable prices.
products.
Doors and windows for any style, with Republic products.
Stylish windows and doors for any interior, from Republic company.
Discounts on window and door solutions, from experienced specialists.
Quality windows and doors for your home, with Republic products.
New solutions from Republic, for your convenience.
Don’t settle for less, by Republic company.
Reduce your energy bills, with products.
Create coziness in your home, with windows and doors.
Experts in windows and doors, by Republic.
sliding doors near me [url=https://wearehoist.com/sliding-doors-melbourne/]https://wearehoist.com/sliding-doors-melbourne/[/url] .
мостбет приложение узбекистан [url=http://mostbet4005.ru/]http://mostbet4005.ru/[/url]
скачат мостбет [url=https://www.mostbet4015.ru]https://www.mostbet4015.ru[/url]
сколько стоит игровой компьютер [url=www.kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter3.ru/]www.kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter3.ru/[/url] .
mostbet [url=www.mostbet4006.ru]www.mostbet4006.ru[/url]
где заказать проект перепланировки квартиры [url=http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry13.ru]http://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry13.ru[/url] .
мочтбет [url=mostbet4006.ru]mostbet4006.ru[/url]
888starz официальный сайт скачать бесплатно [url=http://www.888starz-skachat-na-android.com]888starz официальный сайт скачать бесплатно[/url] .
клубная музыка 2023 [url=www.klubnaya-muzyka30.ru/]www.klubnaya-muzyka30.ru/[/url] .
красивый игровой пк [url=https://kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter3.ru]https://kupit-igrovoj-kompyuter3.ru[/url] .
www. mostbet. com [url=www.mostbet4015.ru]www.mostbet4015.ru[/url]
télécharger 1win [url=1win3008.com]1win3008.com[/url]
перепланировка квартиры дизайн проект [url=https://proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry13.ru/]proekt-pereplanirovki-kvartiry13.ru[/url] .
Moreover, ordering balloons for delivery has never been easier. With just a few clicks, you can select your preferred designs and schedule a delivery time. This convenience means that anyone can enjoy the beauty of balloons without the hassle.
inflated valentines balloons [url=http://www.bestwedding-video.com/product-category/valentines-balloons/]http://www.bestwedding-video.com/product-category/valentines-balloons/[/url] .
скачать мостбет на телефон [url=mostbet4016.ru]mostbet4016.ru[/url]
1win usa [url=www.1win3008.com]1win usa[/url]
dj онлайн [url=http://www.klubnaya-muzyka30.ru]dj онлайн[/url] .
мостбет техподдержка [url=mostbet4005.ru]mostbet4005.ru[/url]
mostbet kripto orqali depozit [url=mostbet4008.ru]mostbet4008.ru[/url]
mostbet uz telegram qo‘llab-quvvatlash [url=https://www.mostbet4007.ru]https://www.mostbet4007.ru[/url]
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам. Мы предлагаем документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей России. Дипломы и аттестаты делаются на “правильной” бумаге самого высокого качества. Это позволяет делать настоящие дипломы, не отличимые от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-5v-gorode-ufa-2.ru/]orikdok-5v-gorode-ufa-2.ru[/url]
mostbet uz apk skachat [url=www.mostbet4007.ru]www.mostbet4007.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом ВУЗа по невысокой стоимости вы можете, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной фирме. Заказать документ о получении высшего образования вы можете у нас в столице. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-vologda-35.ru/]orikdok-1v-gorode-vologda-35.ru[/url]
Купить диплом о высшем образовании. Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через проверенную и надежную фирму дарит ряд преимуществ. Данное решение помогает сберечь время и существенные средства. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-vladivostok-25.online/]orikdok-1v-gorode-vladivostok-25.online[/url]
1win aviator login [url=http://1win3010.com]1win aviator login[/url]
диплом специалиста купить [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru/]диплом специалиста купить[/url] .
диплом инженера купить [url=http://www.arus-diplom5.ru]диплом инженера купить[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4792 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom3.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
1win bonus [url=1win3010.com]1win3010.com[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4161 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor2.ru/]Купить диплом Россия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 999 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor3.ru/]Купить диплом Москва[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1086 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor5.ru/]http://inforepetitor5.ru/[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
mostbet официальный сайт скачать [url=http://mostbet4017.ru/]http://mostbet4017.ru/[/url]
mostbet qiwi to‘lov uz [url=http://mostbet4009.ru]http://mostbet4009.ru[/url]
most-bet [url=http://mostbet4008.ru]http://mostbet4008.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом института по доступной цене можно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной компании. Заказать документ о получении высшего образования вы можете у нас в Москве. [url=http://orikdok-3v-gorode-groznyy-20.ru/]orikdok-3v-gorode-groznyy-20.ru[/url]
Приобрести документ ВУЗа вы имеете возможность у нас в столице. Купить диплом университета по невысокой стоимости возможно, обращаясь к надежной специализированной фирме. [url=http://officaldrp.forumex.ru/viewtopic.phpf=23&t=759/]officaldrp.forumex.ru/viewtopic.phpf=23&t=759[/url]
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по выгодным тарифам— [url=http://diplomist.com/]diplomist.com[/url]
Приобрести диплом университета. Заказ документа о высшем образовании через проверенную и надежную компанию дарит ряд преимуществ для покупателя. Такое решение позволяет сэкономить как дорогое время, так и серьезные денежные средства. [url=http://orikdok-2v-gorode-astrakhan-30.online/]orikdok-2v-gorode-astrakhan-30.online[/url]
Купить диплом на заказ в столице возможно через официальный сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-3v-gorode-krasnodar-23.ru/]orikdok-3v-gorode-krasnodar-23.ru[/url]
putas Valencia [url=http://www.vipescortsvalencia.com]http://www.vipescortsvalencia.com[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4529 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom4.ru/]Ознакомиться здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
мостбет войти [url=www.mostbet4010.ru]мостбет войти[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4033 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor3.ru/]Диплом цена[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2399 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor2.ru/]Пишите[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом купить цена [url=www.arus-diplom7.ru]диплом купить цена[/url] .
мостбет регистрация [url=https://mostbet4019.ru]https://mostbet4019.ru[/url]
аттестат в челябинске купить [url=www.arus-diplom5.ru]аттестат в челябинске купить[/url] .
mostbet skachat 2024 [url=www.mbtest123.ru]www.mbtest123.ru[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2141 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom6.ru/]Звоните[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
скачать мостбет кг [url=https://mostbet4020.ru]https://mostbet4020.ru[/url]
диджеи электронной музыки [url=www.klubnaya-muzyka32.ru]диджеи электронной музыки[/url] .
escort en valencia [url=http://www.vipescortsvalencia.com]http://www.vipescortsvalencia.com[/url] .
mostbet официальный сайт скачать [url=http://mostbet11003.ru/]http://mostbet11003.ru/[/url]
мостюет [url=http://mostbet11003.ru/]http://mostbet11003.ru/[/url]
скачать мостбет кыргызстан [url=mostbet4020.ru]mostbet4020.ru[/url]
mostbet official [url=https://www.mostbet4019.ru]https://www.mostbet4019.ru[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по доступным тарифам. Приобретение документа, который подтверждает обучение в ВУЗе, – это разумное решение. Купить диплом о высшем образовании: [url=http://youslade.com/read-blog/101884_kupit-diplom-o-vysshem-obrazovanii-v-moskve.html/]youslade.com/read-blog/101884_kupit-diplom-o-vysshem-obrazovanii-v-moskve.html[/url]
bananastreet [url=http://www.klubnaya-muzyka32.ru]bananastreet[/url] .
что такое мостбет [url=www.mostbet11007.ru]www.mostbet11007.ru[/url]
мостбет сом [url=http://mostbet11006.ru/]http://mostbet11006.ru/[/url]
производство значков [url=https://znacki-na-zakaz.ru/]производство значков[/url] .
мостбет скачать на андроид [url=http://mostbet11006.ru/]http://mostbet11006.ru/[/url]
мостбет [url=http://mostbet11002.ru/]http://mostbet11002.ru/[/url]
мостбет. вход. [url=https://mostbet11002.ru]https://mostbet11002.ru[/url]
mostbet ru [url=http://mostbet4010.ru/]http://mostbet4010.ru/[/url]
Заказать документ о получении высшего образования можно в нашем сервисе. Приобрести диплом университета по выгодной стоимости можно, обратившись к надежной специализированной фирме. [url=http://t-net.si/2025/05/13/kak-bystro-i-bezopasno-kupit-diplom-v-rossii-91/]t-net.si/2025/05/13/kak-bystro-i-bezopasno-kupit-diplom-v-rossii-91[/url]
Наша компания предлагает выгодно и быстро купить диплом, который выполняется на оригинальной бумаге и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Данный документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при использовании специфических приборов. [url=http://tiwlo.com/read-blog/1_diplom-o-srednem-obrazovanii-kupit.html/]tiwlo.com/read-blog/1_diplom-o-srednem-obrazovanii-kupit.html[/url]
значки из латуни на заказ [url=https://znacki-na-zakaz.ru/]https://znacki-na-zakaz.ru/[/url] .
мостбеь [url=http://mostbet11005.ru/]мостбеь[/url]
купить аттестат в белгороде [url=http://www.arus-diplom3.ru]купить аттестат в белгороде[/url] .
Мы можем предложить документы любых учебных заведений, которые находятся в любом регионе РФ. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://comptonrpp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=3877/]comptonrpp.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=6&t=3877[/url]
мостбет. регистрация. [url=https://mostbet11005.ru]https://mostbet11005.ru[/url]
скачать mostbet [url=https://mostbet11007.ru/]https://mostbet11007.ru/[/url]
mental health ai chatbot [url=http://mental-health5.com]http://mental-health5.com[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3179 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor7.ru/]Купить диплом нового образца[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом педагогический [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru]http://arus-diplom8.ru[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4211 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom7.ru/]http://spbrcom7.ru/[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
мостбет ставки онлайн [url=https://mostbet11010.ru/]https://mostbet11010.ru/[/url]
изготовление металлических значков [url=www.znacki-na-zakaz1.ru]изготовление металлических значков[/url] .
новый диплом купить [url=https://www.arus-diplom4.ru]https://www.arus-diplom4.ru[/url] .
мостбет букмекерская контора [url=https://www.mostbet11013.ru]https://www.mostbet11013.ru[/url]
сделать металлический значок на заказ [url=http://www.znacki-na-zakaz2.ru]http://www.znacki-na-zakaz2.ru[/url] .
ставки мостбет [url=mostbet11012.ru]mostbet11012.ru[/url]
mostbet com вход [url=https://www.mostbet11012.ru]https://www.mostbet11012.ru[/url]
мостбет com [url=mostbet11009.ru]мостбет com[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3005 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor9.ru/]Пишите[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2277 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom10.ru/]Смотреть тут[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4867 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom9.ru/]По ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1879 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor8.ru/]На сайте[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом о высшем образовании в москве [url=https://www.arus-diplom3.ru]купить диплом о высшем образовании в москве[/url] .
металлические пины [url=www.znacki-na-zakaz1.ru/]www.znacki-na-zakaz1.ru/[/url] .
казино онлайн [url=https://kazino-online-rb.by]казино онлайн[/url] .
mostbet.com скачать [url=https://www.mostbet11001.ru]https://www.mostbet11001.ru[/url]
Своевременная [url=https://poverkoff.ru/]поверка в Москве[/url] — это залог стабильной работы оборудования и безопасности. Все документы оформляются по форме.
Поверка средств измерений — это важный процесс, который позволяет обеспечить точность измерений в различных областях. Данный процесс обеспечивает соответствие оборудования установленным нормам и стандартам качества.
Существует несколько этапов поверки, которые включают в себя оценку состояния измерительных приборов. Следующим шагом является выполнение контрольных измерений и их сравнение с эталонными показателями. В случае несоответствий прибор нужно откалибровать или заменить на другой.
Важно помнить, что поверка средств измерений должна проводиться регулярно для обеспечения их точности. Важно контролировать сроки поверки, чтобы обеспечить правильность и достоверность измерений.
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Заказать диплом любого университета:
[url=http://c90226sl.beget.tech/2025/05/29/vash-put-k-uspeshnoj-karere-nachinaetsya-zdes/]c90226sl.beget.tech/2025/05/29/vash-put-k-uspeshnoj-karere-nachinaetsya-zdes[/url]
металлические пины на заказ [url=www.znacki-na-zakaz2.ru/]www.znacki-na-zakaz2.ru/[/url] .
скачать мостбет казино [url=https://mostbet11001.ru/]https://mostbet11001.ru/[/url]
Купить диплом ВУЗа по доступной цене вы можете, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной компании. Приобрести документ о получении высшего образования вы сможете в нашей компании в Москве. [url=http://orikdok-2v-gorode-kaliningrad-39.online/]orikdok-2v-gorode-kaliningrad-39.online[/url]
мостбет ком вход [url=http://mostbet11009.ru]http://mostbet11009.ru[/url]
букмекер кыргызстан [url=mostbet11011.ru]mostbet11011.ru[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по выгодным тарифам. Покупка документа, который подтверждает обучение в университете, – это грамотное решение. Заказать диплом любого университета: [url=http://massgrowpoultry.co.za/2025/06/16/kupit-diplom-legko-i-bystro-230/]massgrowpoultry.co.za/2025/06/16/kupit-diplom-legko-i-bystro-230[/url]
водопонижение для строительства [url=www.skoleoz.borda.ru/?1-2-0-00001894-000-0-0-1750670530]водопонижение для строительства[/url] .
A major benefit of using a natural terpene blend is its capability to boost cannabinoid effects. The entourage effect describes how terpenes and cannabinoids interact to create a more potent overall effect.
terpene blends uk [url=http://chinese-shipments.com]http://chinese-shipments.com[/url] .
официальный сайт mostbet [url=https://mostbet11010.ru/]https://mostbet11010.ru/[/url]
mostber [url=http://mostbet11011.ru/]http://mostbet11011.ru/[/url]
Приобрести диплом об образовании. Покупка документа о высшем образовании через проверенную и надежную фирму дарит много плюсов для покупателя. Данное решение дает возможность сэкономить время и существенные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-v-gorode-volgograd-34.ru/]orikdok-v-gorode-volgograd-34.ru[/url]
Купить диплом на заказ вы сможете используя официальный портал компании. [url=http://orikdok-3v-gorode-vladikavkaz-15.online/]orikdok-3v-gorode-vladikavkaz-15.online[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2465 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor9.ru/]Купить диплом недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4946 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom10.ru/]Обращайтесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3935 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom9.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. Для нас важно, чтобы документы были доступными для большинства наших граждан. Заказать диплом об образовании [url=http://melocasting.com/employer/premialnie-diplom-24/]melocasting.com/employer/premialnie-diplom-24[/url]
Мы предлагаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по доступным тарифам. Цена может зависеть от выбранной специальности, года выпуска и университета: [url=http://facebook.scripts-buying.com/read-blog/480_kupit-diplom-o-vysshem-obrazovanii-reestr.html/]facebook.scripts-buying.com/read-blog/480_kupit-diplom-o-vysshem-obrazovanii-reestr.html[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1449 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf2.ru/]Здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом в биробиджане [url=http://arus-diplom4.ru]купить диплом в биробиджане[/url] .
авиатор казино [url=http://1win11001.ru]http://1win11001.ru[/url]
как зайти на сайт мостбет [url=https://mostbet11014.ru]https://mostbet11014.ru[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам. Мы готовы предложить документы техникумов, расположенных на территории всей Российской Федерации. Дипломы и аттестаты выпускаются на бумаге высшего качества. Это позволяет делать настоящие дипломы, которые невозможно отличить от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-3v-gorode-chelyabinsk-74.ru/]orikdok-3v-gorode-chelyabinsk-74.ru[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2324 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom8.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
codigo 1win [url=1win3002.com]codigo 1win[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1461 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom7.ru/]Смотреть тут[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом психолога [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru/]купить диплом психолога[/url] .
мостбет контакты [url=mostbet11014.ru]mostbet11014.ru[/url]
заказать водопонижение иглофильтрами [url=http://www.4dkp.forum24.ru/?1-18-0-00005163-000-0-0-1750670206]заказать водопонижение иглофильтрами[/url] .
заказать водопонижение иглофильтрами [url=http://mymoscow.forum24.ru/?1-6-0-00030109-000-0-0-1750668227]заказать водопонижение иглофильтрами[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3786 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor6.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Гороскоп [url=85goelro.ru]85goelro.ru[/url] .
Какой сегодня церковный праздник [url=https://tti-sfedu.ru/]https://tti-sfedu.ru/[/url] .
Пронедра [url=congress-st.ru]congress-st.ru[/url] .
смета на водопонижение иглофильтрами [url=www.rodoslav.forum24.ru/?1-4-0-00001086-000-0-0-1750667814/]смета на водопонижение иглофильтрами[/url] .
Узнайте [url=https://genuborkachistota.ru/]сколько стоит клининг в Москве[/url] при различных форматах заказа. Цена рассчитывается персонально и не меняется без согласования.
В последние годы клининг в Москве становится все более востребованным. Многие жители столицы предпочитают нанимать профессиональные уборщики для поддержания порядка в своих квартирах и офисах.
Цены на клининг могут варьироваться в зависимости от специфики услуг. Уборка квартиры, как правило, обойдется от 1500 до 5000 рублей в зависимости от площади.
Клининговые компании предлагают дополнительные услуги, такие как мойка окон и чистка мебели. Стоимость дополнительных услуг может существенно сказаться на общей цене уборки.
Прежде чем остановиться на конкретной клининговой компании, будет полезно изучить предложения на рынке. Важно учитывать мнения клиентов и репутацию компании.
Приобрести диплом на заказ в столице вы можете через сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-3v-gorode-yoshkar-ola-12.ru/]orikdok-3v-gorode-yoshkar-ola-12.ru[/url]
1 вин букмекерская [url=https://www.1win11003.ru]https://www.1win11003.ru[/url]
Какой сегодня праздник [url=www.allizmalkovo.ru]www.allizmalkovo.ru[/url] .
The process of moving can be intimidating for a lot of people and families. Yet, having access to professional moving services can help make the experience smoother.
cheap moving companies in austin tx [url=http://trafficarbitration.com/austin-movers/]http://trafficarbitration.com/austin-movers/[/url] .
Календарь стрижек [url=https://85goelro.ru]https://85goelro.ru[/url] .
Погода [url=http://tti-sfedu.ru/]http://tti-sfedu.ru/[/url] .
1 вин ставки на спорт [url=https://www.1win11001.ru]https://www.1win11001.ru[/url]
1win ставка [url=http://1win11003.ru]http://1win11003.ru[/url]
Заказ подходящего диплома через качественную и надежную фирму дарит ряд плюсов. Приобрести диплом: [url=http://pytalovo.4admins.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=15&sid=2251e0c771090a8f42680298229936fe]pytalovo.4admins.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=15&sid=2251e0c771090a8f42680298229936fe[/url]
Магнитные бури [url=www.congress-st.ru]www.congress-st.ru[/url] .
медицинский диплом купить в москве [url=arus-diplom1.ru]arus-diplom1.ru[/url] .
Вы заказываете документ через надежную и проверенную компанию. Заказать диплом института– [url=http://m-s-r.ru/kupite-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-po-vigodnoj-tsene/]m-s-r.ru/kupite-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-po-vigodnoj-tsene/[/url]
букмекерские конторы бишкек [url=http://mostbet11026.ru/]http://mostbet11026.ru/[/url]
Приобрести документ университета можно у нас в Москве. Купить диплом университета по выгодной цене можно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной компании. [url=http://133636.activeboard.com/forum.spark/]133636.activeboard.com/forum.spark[/url]
Приобрести диплом об образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам— [url=http://nnpages.ru/]nnpages.ru[/url]
1win. casino. [url=http://1win3002.com]http://1win3002.com[/url]
мостбет букмекерская контора [url=mostbet11025.ru]mostbet11025.ru[/url]
Купить диплом института по невысокой стоимости вы можете, обратившись к надежной специализированной фирме. Мы готовы предложить документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. [url=http://10000diplomov.ru/kupite-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-bistro-i-legko/]10000diplomov.ru/kupite-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-bistro-i-legko/[/url]
Где приобрести диплом по актуальной специальности?
Купить диплом университета по доступной стоимости можно, обращаясь к надежной специализированной фирме.: [url=http://institute-diplom.ru/]institute-diplom.ru[/url]
mostbet ckachat [url=https://www.mostbet11024.ru]https://www.mostbet11024.ru[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным тарифам. Дипломы производятся на оригинальных бланках Заказать диплом института [url=http://dip-lom-rus.ru/]dip-lom-rus.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа!
Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через надежную компанию дарит много плюсов для покупателя. Заказать диплом любого университета у сильной фирмы: [url=http://doks-v-gorode-severodvinsk-29.ru/]doks-v-gorode-severodvinsk-29.ru[/url]
мостбет скачать на компьютер [url=https://mostbet11024.ru]мостбет скачать на компьютер[/url]
Какой сегодня праздник [url=http://dorogi34.ru]http://dorogi34.ru[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1399 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf7.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Awesome! This is a genuinely remarkable post. I got a clear idea from it.
mostbet скачать на телефон [url=http://mostbet11025.ru]http://mostbet11025.ru[/url]
диплом купить в пензе [url=https://arus-diplom5.ru/]https://arus-diplom5.ru/[/url] .
Наслаждайтесь любимыми блюдами, не выходя из дома — [url=https://sushiyok.ru/]доставка ролл СПб[/url] порадует качеством и точностью.
Заказать суши довольно просто. Существует множество способов сделать это: от онлайн-приложений до звонка в ресторан. Каждый вариант имеет свои преимущества и недостатки.
При выборе ресторана обратите внимание на отзывы. Почитайте, что говорят люди о качестве еды и обслуживании. Такой подход позволяет минимизировать риски и сделать правильный выбор.
Не забудьте обратить внимание на меню ресторана. Разные рестораны могут предлагать различные варианты суши и роллов. Выбор уникальных и необычных позиций может сделать ваш вечер интереснее.
После оформления заказа уточните время доставки. Уточнение времени доставки поможет избежать ожидания и обеспечит комфортное времяпрепровождение. Также важно узнать, есть ли доставка в вашу местность.
История дня [url=https://dorogi34.ru/]https://dorogi34.ru/[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2622 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf4.ru/]Дипломы о высшем образовании купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2328 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf9.ru/]Звоните[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат можно ли [url=www.arus-diplom6.ru]купить аттестат можно ли[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4813 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf6.ru/]Купить государственный диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Заказать документ института вы имеете возможность у нас в Москве. Купить диплом университета по невысокой стоимости возможно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной фирме. [url=http://recruit.brainet.co.za/companies/frees-diplom/]recruit.brainet.co.za/companies/frees-diplom[/url]
букмекерские конторы в кыргызстане [url=mostbet11030.ru]mostbet11030.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании. Покупка документа о высшем образовании через надежную компанию дарит много преимуществ для покупателя. Это решение дает возможность сберечь как длительное время, так и значительные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-5v-gorode-samara-63.ru/]orikdok-5v-gorode-samara-63.ru[/url]
букмекеры кыргызстана [url=http://mostbet11029.ru]букмекеры кыргызстана[/url]
Приобрести диплом вы имеете возможность используя официальный сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-bryansk-32.ru/]orikdok-1v-gorode-bryansk-32.ru[/url]
теннесси бк скачать [url=https://mostbet11030.ru/]https://mostbet11030.ru/[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3774 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf7.ru/]Доступ по ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые находятся на территории всей России. Купить диплом ВУЗа:
[url=http://gooalsocial.com/blogs/view/9640/]gooalsocial.com/blogs/view/9640[/url]
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по доступным ценам. Приобретение документа, подтверждающего окончание ВУЗа, – это выгодное решение. Купить диплом любого ВУЗа: [url=http://robototehnika.ru/communication/forum/user/28903/]robototehnika.ru/communication/forum/user/28903[/url]
купить диплом в калуге [url=http://www.arus-diplom2.ru]купить диплом в калуге[/url] .
mostbet skacat [url=https://www.mostbet11022.ru]https://www.mostbet11022.ru[/url]
купить диплом училища [url=http://www.arus-diplom5.ru]http://www.arus-diplom5.ru[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1193 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf3.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1489 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf9.ru/]Пишите нам[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2101 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf10.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1373 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf5.ru/]Пишите[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3759 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf6.ru/]Мы поможем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых ВУЗов Российской Федерации. Документы производятся на фирменных бланках. [url=http://all-smeta.ru/?sid=cad73a3ae085603d674496e1bd7ebd9b/]all-smeta.ru/?sid=cad73a3ae085603d674496e1bd7ebd9b[/url]
Приобрести диплом университета по выгодной цене можно, обратившись к надежной специализированной фирме. Заказать диплом: [url=http://eggerland.com/vash-uspeh-nachinaetsja-s-diploma-196/]eggerland.com/vash-uspeh-nachinaetsja-s-diploma-196[/url]
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, которые находятся в любом регионе России. Дипломы и аттестаты печатаются на бумаге самого высшего качества: [url=http://guiltyworld.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=5571/]guiltyworld.getbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=5571[/url]
диплом купить в нижнем новгороде [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru]диплом купить в нижнем новгороде[/url] .
Reasons why you should hire a licensed electrician for services related to residential electrical repairs
Dealing with this kind of electrical work on your own can be dangerous. Even though it may seem simple, it’s best to trust a certified electrician to get the job done to code.
Certified experts have the tools and background needed to fix hidden issues that DIYers may miss. Using an expert means the job is completed safely and follows all safety standards.
In the end, it’s the smarter choice to call on a licensed electrician for your repair needs. You’ll gain professional results and avoid future problems.
[url=https://danmatthewselectric.com/contact-us]electric panel upgrade Campbell[/url]
[url=http://moneyh2o.com/2023/10/29/hello-world/]Don’t risk a fire: The importance of a licensed electrician for emergency switch panel service[/url] 7_665db
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1629 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor10.ru/]Перейти[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1793 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf7.ru/]Купить диплом нового образца[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
mostbet skachat 2024 [url=https://www.mostbet11022.ru]mostbet skachat 2024[/url]
ставки на спорт бишкек [url=https://mostbet11018.ru/]https://mostbet11018.ru/[/url]
мостбет ставки на спорт скачать [url=https://mostbet11018.ru]https://mostbet11018.ru[/url]
1win официальный сайт мобильная [url=1win1106.ru]1win1106.ru[/url]
ставки на мостбет [url=https://www.mostbet11029.ru]https://www.mostbet11029.ru[/url]
скачать 1win [url=http://1win1104.ru/]http://1win1104.ru/[/url]
авиатор 1win играть [url=1win1105.ru]1win1105.ru[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1853 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor10.ru/]Обращайтесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Заказать диплом любого института. Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через надежную компанию дарит ряд плюсов для покупателя. Такое решение помогает сберечь время и существенные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-v-gorode-kemerovo-42.online/]orikdok-v-gorode-kemerovo-42.online[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам. Мы можем предложить документы техникумов, расположенных в любом регионе России. Дипломы и аттестаты делаются на бумаге высшего качества. Это дает возможности делать государственные дипломы, которые невозможно отличить от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-chelyabinsk-74.ru/]orikdok-1v-gorode-chelyabinsk-74.ru[/url]
1win скачать бесплатно [url=1win1104.ru]1win1104.ru[/url]
1win это что [url=https://1win1105.ru]https://1win1105.ru[/url]
диплом купить в казани [url=http://arus-diplom3.ru]диплом купить в казани[/url] .
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам— [url=http://rus-pages.ru/]rus-pages.ru[/url]
Türkçe dublajlı ve 4K kalitesindeki filmlerimiz, izleyicilere her zaman en iyi deneyimi sunmak için titizlikle seçiliyor. [url=https://onlinefilmturk.com/]turkce dublaj filmler 4k[/url] kategorimiz, farklı türlerdeki yapımlarla dopdolu, favori filmlerinizi en yüksek kalitede izleme imkanı tanıyor. Her anınızda yanınızdayız.
Dijital yayın çağında filmleri yüksek çözünürlükte izlemek artık standart bir beklenti haline geldi. Full HD filmler canlı görseller ve olağanüstü netlik sunarak büyük ilgi görüyor.
Çevrimiçi film izlemek isteyenler için Full HD film izle 4k gibi seçenekler mevcut. Çoğu yayın hizmeti, her izleyiciye hitap edecek şekilde geniş arşivler oluşturur.
Keyifli bir film deneyimi için güvenilir platformları tercih etmek oldukça önemlidir. Düşük kaliteli içeriklerden kaçınmak için platformların itibarını araştırmak akıllıca olacaktır.
Full HD ve 4k kalitesinde film izlemek, evdeki genel izleme keyfinizi artırabilir. Arkadaşlarınızla bir film gecesi planlayın ve 4k Full HD filmlerin sunduğu muhteşem görüntü kalitesinin tadını çıkarın.
mostbet.com казино скачать [url=https://mostbet11017.ru/]https://mostbet11017.ru/[/url]
mostbet сайт [url=mostbet11016.ru]mostbet11016.ru[/url]
Купить диплом университета по доступной цене вы можете, обращаясь к надежной специализированной компании. Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов России. Купить диплом о высшем образовании– [url=http://git.fuwafuwa.moe/thomasshaw9688/My-List/issues/new/]git.fuwafuwa.moe/thomasshaw9688/My-List/issues/new[/url]
1win слоты скачать на андроид бесплатно [url=https://1win1107.ru]https://1win1107.ru[/url]
скачать mostbet на телефон [url=http://mostbet11017.ru/]http://mostbet11017.ru/[/url]
1вин сайт [url=www.1win1106.ru]1вин сайт[/url]
how to withdraw from 1win [url=https://1win11001.com]https://1win11001.com[/url]
как потратить бонусы на спорт в 1вин [url=https://1win1111.ru]https://1win1111.ru[/url]
1 win.pro [url=https://www.1win1110.ru]https://www.1win1110.ru[/url]
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://bluedom.fr/employer/diplomirovans/]bluedom.fr/employer/diplomirovans[/url]
1вин промокоды [url=http://1win1111.ru]1вин промокоды[/url]
1win login ug [url=https://www.1win11003.com]https://www.1win11003.com[/url]
1win casino ug [url=https://1win11003.com/]https://1win11003.com/[/url]
1win букмекерская контора вход [url=www.1win1109.ru]www.1win1109.ru[/url]
Вы приобретаете документ через надежную и проверенную фирму. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании– [url=http://mexschool.ru/kupit-nastoyashij-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-3/]mexschool.ru/kupit-nastoyashij-diplom-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr-3/[/url]
купить диплом в майкопе [url=http://arus-diplom1.ru/]купить диплом в майкопе[/url] .
1win бонусы [url=https://www.1win1109.ru]https://www.1win1109.ru[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4526 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor12.ru/]Купить диплом недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
???? 888starz [url=www.egypt888starz.net/]www.egypt888starz.net/[/url] .
моствет [url=https://mostbet11019.ru/]https://mostbet11019.ru/[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2497 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor14.ru/]Купить диплом недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
1win apk [url=https://1win11002.com/]1win apk[/url]
скачать мостбет кг [url=http://mostbet11019.ru/]http://mostbet11019.ru/[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4139 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom15.ru/]Мы поможем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом в оренбурге [url=www.arus-diplom3.ru]купить диплом в оренбурге[/url] .
promo code for 1win [url=http://1win11002.com/]http://1win11002.com/[/url]
Приобрести диплом университета по доступной цене вы можете, обратившись к надежной специализированной компании. Мы готовы предложить документы высших учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. [url=http://kommunikatory.ru/kupit-diplom-s-vneseniem-v-reestr-bistro-i-nadezhno-2/]kommunikatory.ru/kupit-diplom-s-vneseniem-v-reestr-bistro-i-nadezhno-2/[/url]
This is a masterpiece of a blog post.
букмекерская контора 1win [url=http://1win1110.ru/]букмекерская контора 1win[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4319 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom14.ru/]Звоните[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2901 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom11.ru/]Узнать условия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4761 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor15.ru/]Купить диплом Россия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2345 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom12.ru/]Диплом цена[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4364 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor11.ru/]Пишите[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
бонусы на казино 1win [url=www.1win1114.ru]www.1win1114.ru[/url]
1 win казино скачать [url=https://1win1114.ru]https://1win1114.ru[/url]
Приобретение диплома ВУЗа через проверенную и надежную компанию дарит множество преимуществ. Быстро купить диплом о высшем образовании: [url=http://finansi.5nx.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1750]finansi.5nx.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=1750[/url]
how to play mines on 1win [url=http://1win11005.com]how to play mines on 1win[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2807 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor14.ru/]Купить диплом института[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
промокод 1хставка [url=http://1win1109.ru/]http://1win1109.ru/[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1310 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom15.ru/]Сайт компании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестаты за 11 класс [url=http://www.arus-diplom2.ru]http://www.arus-diplom2.ru[/url] .
1 вин ставки на спорт зеркало [url=http://1win1109.ru]http://1win1109.ru[/url]
Приобрести диплом института. Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через надежную компанию дарит ряд преимуществ для покупателя. Такое решение позволяет сберечь время и значительные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-ulyanovsk-73.online/]orikdok-1v-gorode-ulyanovsk-73.online[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1499 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom14.ru/]Узнать условия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Удобный подбор, консультации и доставка по всей России. Вы можете [url=https://magazin-nootropov.ru/]ноотропы купить в Москве[/url] прямо сейчас с гарантией качества.
Ноотропы представляют собой группу препаратов, способствующих улучшению умственной деятельности. Ноотропы используются для стимуляции умственной активности, улучшения памяти и повышения уровня внимания.
Существует множество видов ноотропов, как синтетических, так и природных. Все эти препараты различаются по своим механизму действия и конечным результатам.
Природные источники ноотропов, например, женьшень и гинкго билоба, славятся своими благотворными свойствами. Они часто используются в традиционной медицине для улучшения памяти и сосредоточенности.
Среди синтетических ноотропов, таких как пирацетам, выделяются препараты, обладающие специфическими действиями. Эти средства активно используют для терапии различных когнитивных нарушений, например, проблем с памятью.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4617 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor15.ru/]Мы поможем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2826 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom12.ru/]Обращайтесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4919 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom13.ru/]Купить диплом Россия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
icra müdürlüğü sınavı 2025
1xставка промокод [url=http://1win1113.ru/]1xставка промокод[/url]
Купить документ о получении высшего образования вы сможете в нашей компании в Москве. Приобрести диплом университета по доступной цене возможно, обратившись к надежной специализированной компании. [url=http://moydesignstudio.com/kak-bystro-i-bezopasno-kupit-diplom-v-rossii-152/]moydesignstudio.com/kak-bystro-i-bezopasno-kupit-diplom-v-rossii-152[/url]
1win aviator [url=http://1win11005.com]http://1win11005.com[/url]
Где купить диплом специалиста?
Заказать диплом института по выгодной стоимости можно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной компании.: [url=http://diplom-insti.ru/]diplom-insti.ru[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по невысоким ценам. Дипломы производятся на подлинных бланках Купить диплом любого института [url=http://diplomj-irkutsk.ru/]diplomj-irkutsk.ru[/url]
Приобрести диплом об образовании!
Приобретение официального диплома через качественную и надежную компанию дарит ряд достоинств. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа у надежной компании: [url=http://doks-v-gorode-ryazan-62.online/]doks-v-gorode-ryazan-62.online[/url]
1win 500% [url=https://1win1113.ru]https://1win1113.ru[/url]
Заказать документ ВУЗа вы можете в нашей компании в столице. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых университетов РФ. Даем гарантию, что при проверке документов работодателями, каких-либо подозрений не появится. [url=http://cardinalparkmld.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=1872/]cardinalparkmld.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=3&t=1872[/url]
мелбет отзывы 2022 [url=http://mostbet11021.ru]http://mostbet11021.ru[/url]
1win контора зеркало сайта [url=https://1win22095.ru/]1win контора зеркало сайта[/url]
1win дзеркало [url=1win22095.ru]1win дзеркало[/url]
Лучшие предложения по аренде жилья на лето 2025 в Туапсе уже доступны. Успейте забронировать понравившийся объект до наплыва туристов [url=https://otdyh-v-tuapse.ru/]снять жилье в туапсе 2025[/url].
Туапсе предлагает отличный отдых на фоне живописного черного моря. На этом курорте вас ждут удивительные пляжи и комфортная погода.
Летом здесь множество туристов, кто приезжает для расслабления и активного отдыха. Отдыхающие могут наслаждаться множеством развлечений, начиная от водных активностей и заканчивая культурными программами.
В Туапсе вы найдете разнообразные отели и гостевые дома на любой вкус. Цены на проживание варьируются, что дает возможность выбрать комфортный вариант для любого бюджета.
Не упустите возможность исследовать интересные места и природные парки региона. Это подарит вам незабываемые впечатления и возможность познакомиться с природой края.
купить аттестат ссср [url=https://arus-diplom4.ru]купить аттестат ссср[/url] .
купить диплом колледжа [url=http://arus-diplom5.ru]купить диплом колледжа[/url] .
1win.online [url=1win22096.ru]1win22096.ru[/url]
бк 1 вин официальный сайт [url=https://www.1win22096.ru]бк 1 вин официальный сайт[/url]
скачать программу melbet на андроид [url=https://mostbet11021.ru]https://mostbet11021.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом под заказ возможно через сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-kostroma-44.ru/]orikdok-4v-gorode-kostroma-44.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом о высшем образовании. Покупка официального диплома через надежную фирму дарит массу достоинств для покупателя. Это решение помогает сберечь как продолжительное время, так и серьезные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-vladivostok-25.ru/]orikdok-1v-gorode-vladivostok-25.ru[/url]
мостбет официальный сайт [url=www.mostbet33010.ru]www.mostbet33010.ru[/url]
mostbet вход в личный кабинет [url=www.mostbet33010.ru]mostbet вход в личный кабинет[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4419 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf11.ru/]Доступ по ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4828 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf12.ru/]Перейти[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Купить диплом возможно через сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-groznyy-20.ru/]orikdok-4v-gorode-groznyy-20.ru[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3393 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom13.ru/]Купить диплом института[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
скачать приложение 1win на андроид [url=https://1win1135.ru/]https://1win1135.ru/[/url]
Заказать диплом любого университета. Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через проверенную и надежную компанию дарит множество достоинств. Это решение дает возможность сэкономить время и существенные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-novokuznetsk-42.ru/]orikdok-1v-gorode-novokuznetsk-42.ru[/url]
1win ставка [url=1win1134.ru]1win ставка[/url]
игра ракета на деньги 1win отзывы [url=https://1win1137.ru/]https://1win1137.ru/[/url]
1win casino официальный сайт скачать [url=http://1win1137.ru/]http://1win1137.ru/[/url]
1win промокод при регистрации [url=https://1win1134.ru/]1win промокод при регистрации[/url]
1win aviator download [url=http://1win1136.ru]1win aviator download[/url]
игра авиатор как выиграть [url=1win1131.ru]игра авиатор как выиграть[/url]
1win официальный мобильная [url=https://1win1136.ru]https://1win1136.ru[/url]
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр [url=www.arus-diplom8.ru/]купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр[/url] .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным ценам. Мы готовы предложить документы техникумов, которые находятся на территории всей Российской Федерации. Документы выпускаются на бумаге высшего качества. Это дает возможность делать государственные дипломы, которые не отличить от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-nizhniy-novgorod-52.online/]orikdok-4v-gorode-nizhniy-novgorod-52.online[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2231 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf15.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам. Покупка диплома, подтверждающего окончание ВУЗа, – это выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа: [url=http://jobcopusa.com/employer/diplomy-grup-24/]jobcopusa.com/employer/diplomy-grup-24[/url]
Купить диплом института!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по доступным тарифам— [url=http://chel-diplom.ru/]chel-diplom.ru[/url]
1 wın aviator [url=https://www.1win1131.ru]https://www.1win1131.ru[/url]
1win официальный сайт войти [url=www.1win1115.ru]www.1win1115.ru[/url]
Заказать диплом института по доступной цене возможно, обратившись к надежной специализированной компании. Купить документ университета можно в нашей компании в столице. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-krasnoyarsk-24.ru/]orikdok-4v-gorode-krasnoyarsk-24.ru[/url]
что такое бонусы казино в 1win [url=https://1win1132.ru]что такое бонусы казино в 1win[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4715 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf12.ru/]Дипломы о высшем образовании купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей России и СНГ — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 954 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf11.ru/]Пишите нам[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
lucky jet официальный сайт скачать [url=https://www.1win1132.ru]lucky jet официальный сайт скачать[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов в Москве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3819 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom13.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
сколько стоит купить диплом колледжа [url=www.arus-diplom3.ru]www.arus-diplom3.ru[/url] .
1вин регистрация и вход на сайт [url=http://1win1135.ru]http://1win1135.ru[/url]
Купить документ о получении высшего образования вы сможете в нашей компании. Заказать диплом института по выгодной цене можно, обращаясь к надежной специализированной компании. [url=http://testforumrp.forumex.ru/viewtopic.phpf=7&t=536/]testforumrp.forumex.ru/viewtopic.phpf=7&t=536[/url]
купить аттестат в иваново [url=http://arus-diplom5.ru/]купить аттестат в иваново[/url] .
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. Заказ документа, который подтверждает обучение в ВУЗе, – это выгодное решение. Приобрести диплом университета: [url=http://dubainewjobs.com/companies/diplomy-grup-24/]dubainewjobs.com/companies/diplomy-grup-24[/url]
Мы предлагаем дипломы любой профессии по выгодным ценам. Мы предлагаем документы техникумов, расположенных на территории всей России. Документы делаются на “правильной” бумаге самого высшего качества. Это дает возможность делать государственные дипломы, не отличимые от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-v-gorode-chelyabinsk-74.ru/]orikdok-v-gorode-chelyabinsk-74.ru[/url]
Купить диплом института!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по разумным ценам— [url=http://alldirs.ru/]alldirs.ru[/url]
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Купить диплом любого ВУЗа:
[url=http://employme.app/employer/diplomirovans/]employme.app/employer/diplomirovans[/url]
Наши специалисты предлагают выгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполняется на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, водяными знаками, подписями официальных лиц. Диплом пройдет лубую проверку, даже с использованием специфических приборов. [url=http://mm.kabb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=2&sid=7d41790bf3dcd56f2bdc9fac8db137eb/]mm.kabb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=2&sid=7d41790bf3dcd56f2bdc9fac8db137eb[/url]
купить аттестат в москве за 11 класс [url=www.arus-diplom5.ru]купить аттестат в москве за 11 класс[/url] .
win1 aviator [url=https://1win1144.ru]https://1win1144.ru[/url]
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа по доступной цене возможно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной фирме. Приобрести документ о получении высшего образования можно в нашей компании в столице. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-omsk-55.online/]orikdok-1v-gorode-omsk-55.online[/url]
1 win приложение [url=https://1win1145.ru]https://1win1145.ru[/url]
1win установить [url=http://1win1145.ru]http://1win1145.ru[/url]
1win pro download [url=https://1win1143.ru]https://1win1143.ru[/url]
1вин [url=https://1win1144.ru/]https://1win1144.ru/[/url]
Наша компания предлагает выгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на оригинальной бумаге и заверен печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Наш диплом пройдет любые проверки, даже при использовании профессиональных приборов. [url=http://ugolovnichek.ru/dwqa-ask-question/]ugolovnichek.ru/dwqa-ask-question[/url]
1win официальный сайт 1win [url=https://1win1142.ru/]1win официальный сайт 1win[/url]
сколько стоит купить диплом о высшем образовании [url=arus-diplom3.ru]arus-diplom3.ru[/url] .
lucky jet скачать [url=https://1win1143.ru/]https://1win1143.ru/[/url]
Приобрести диплом можно через сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-penza-58.online/]orikdok-4v-gorode-penza-58.online[/url]
как вывести бонусный счет с 1win [url=www.1win1142.ru]как вывести бонусный счет с 1win[/url]
бонусы казино 1win [url=https://1win1141.ru]бонусы казино 1win[/url]
mostbet promo qeydiyyat [url=https://mostbet4046.ru]https://mostbet4046.ru[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по невысоким ценам. Приобретение диплома, который подтверждает обучение в ВУЗе, – это грамотное решение. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании: [url=http://borovsk-tract.maxbb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=1/]borovsk-tract.maxbb.ru/posting.php?mode=post&f=1[/url]
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным тарифам. Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, которые расположены в любом регионе РФ. Документы печатаются на “правильной” бумаге высшего качества. Это дает возможности делать настоящие дипломы, которые не отличить от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-2v-gorode-astrakhan-30.ru/]orikdok-2v-gorode-astrakhan-30.ru[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2096 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom8.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Выгодно приобрести диплом об образовании!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и других профессий по доступным тарифам— [url=http://educationdir.ru/]educationdir.ru[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2764 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom4.su/]Где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 925 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom9.ru/]Сайт компании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3202 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom6.ru/]Где можно купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
mostbet virtual idman [url=www.mostbet4046.ru]www.mostbet4046.ru[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4246 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom1.su/]Купить диплом института высшего образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1786 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom.su/]Купить диплом о образовании недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4914 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom7.ru/]Звоните[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1140 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom2.su/]Узнать подробнее[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом в вологде [url=www.arus-diplom4.ru/]купить диплом в вологде[/url] .
купить диплом педагогический [url=https://arus-diplom7.ru/]https://arus-diplom7.ru/[/url] .
mostbet az apk yüklə [url=www.mostbet4047.ru]www.mostbet4047.ru[/url]
mostbet qeydiyyat pulsuz [url=https://www.mostbet4047.ru]https://www.mostbet4047.ru[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4956 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom5.ru/]Купить диплом с занесением[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1079 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom9.ru/]Диплом об образовании купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1018 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom6.ru/]Купить диплом университета[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
1 win nigeria [url=www.1win3023.com]www.1win3023.com[/url]
Заказать документ о получении высшего образования вы можете в нашей компании в столице. Приобрести диплом университета по выгодной цене можно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной фирме. [url=http://ochag.flybb.ru/viewtopic.phpf=2&t=674/]ochag.flybb.ru/viewtopic.phpf=2&t=674[/url]
Наши специалисты предлагают выгодно и быстро купить диплом, который выполняется на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Данный документ пройдет лубую проверку, даже при помощи профессиональных приборов. [url=http://tookjob.com/profile/cherylgerald09/]tookjob.com/profile/cherylgerald09[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4553 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom.su/]Купить диплом документы[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3477 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom7.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
1win game [url=https://1win3022.com]1win game[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2376 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom2.su/]Купить дипломы[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
1win .com [url=www.1win3023.com]www.1win3023.com[/url]
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа по выгодной цене возможно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной компании. Приобрести документ института вы имеете возможность в нашей компании в Москве. [url=http://orikdok-2v-gorode-smolensk-67.online/]orikdok-2v-gorode-smolensk-67.online[/url]
1win. com [url=https://www.1win3022.com]https://www.1win3022.com[/url]
аттестат в самаре купить [url=http://arus-diplom5.ru/]http://arus-diplom5.ru/[/url] .
Заказать диплом на заказ в Москве вы сможете используя официальный сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-1v-gorode-omsk-55.ru/]orikdok-1v-gorode-omsk-55.ru[/url]
диплом купить о среднем [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru/]диплом купить о среднем[/url] .
купить красный аттестат [url=www.arus-diplom3.ru]www.arus-diplom3.ru[/url] .
Наши специалисты предлагают выгодно и быстро заказать диплом, который выполнен на бланке ГОЗНАКа и заверен мокрыми печатями, штампами, подписями официальных лиц. Документ способен пройти лубую проверку, даже при использовании специально предназначенного оборудования. [url=http://bbs.heyshell.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=55327&extra=/]bbs.heyshell.com/forum.php?mod=viewthread&tid=55327&extra=[/url]
Купить диплом любого института. Приобретение диплома через надежную компанию дарит много преимуществ для покупателя. Такое решение помогает сэкономить время и значительные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-saratov-64.online/]orikdok-4v-gorode-saratov-64.online[/url]
Купить диплом на заказ в Москве возможно через сайт компании. [url=http://orikdok-4v-gorode-krasnodar-23.ru/]orikdok-4v-gorode-krasnodar-23.ru[/url]
диплом горного мастера купить [url=https://arus-diplom4.ru/]https://arus-diplom4.ru/[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3728 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor17.ru/]Открыть[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом в саратове [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru]купить диплом в саратове[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1048 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom17.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем техническом образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4494 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom19.ru/]Куплю диплом в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа по невысокой стоимости можно, обращаясь к проверенной специализированной фирме. Заказать документ о получении высшего образования вы имеете возможность у нас в Москве. [url=http://orikdok-5v-gorode-syktyvkar-11.ru/]orikdok-5v-gorode-syktyvkar-11.ru[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2133 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor20.ru/]Купить диплом недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2162 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor18.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Заказать диплом любого университета. Заказ документа о высшем образовании через надежную компанию дарит ряд достоинств. Это решение помогает сэкономить как личное время, так и серьезные финансовые средства. [url=http://orikdok-3v-gorode-vladivostok-25.ru/]orikdok-3v-gorode-vladivostok-25.ru[/url]
купить диплом об окончании института [url=http://arus-diplom2.ru/]http://arus-diplom2.ru/[/url] .
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам. Купить удостоверение интернатуры — [url=http://kyc-diplom.com/udostoverenie-internatury.html/]kyc-diplom.com/udostoverenie-internatury.html[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3957 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor19.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании цена[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом старого образца купить [url=www.arus-diplom3.ru/]диплом старого образца купить[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1085 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor17.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, которые расположены на территории всей РФ. Заказать диплом любого университета:
[url=http://helpcenter.logintrade.pl/index.php/2025/05/28/kachestvennye-diplomy-dlja-vashego-uspeha-92/]helpcenter.logintrade.pl/index.php/2025/05/28/kachestvennye-diplomy-dlja-vashego-uspeha-92[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4293 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom19.ru/]Купить дипломы в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1885 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom17.ru/]Где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4781 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom18.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4835 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor20.ru/]Диплом о среднем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3090 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor18.ru/]Купить дипломы о высшем образовании цена[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и прочих профессий по приятным тарифам. Цена может зависеть от выбранной специальности, года выпуска и образовательного учреждения: [url=http://4blabla.ru/read-blog/20208_diplom-vuza-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr.html/]4blabla.ru/read-blog/20208_diplom-vuza-s-zaneseniem-v-reestr.html[/url]
I really like reading through a post that can make men and women think. Also, thank you for allowing me to comment!
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2086 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor19.ru/]Здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат в москве за 9 класс [url=arus-diplom8.ru]arus-diplom8.ru[/url] .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. Мы предлагаем документы ВУЗов, которые расположены на территории всей России. Дипломы и аттестаты выпускаются на “правильной” бумаге высшего качества. Это дает возможности делать настоящие дипломы, не отличимые от оригиналов. [url=http://orikdok-5v-gorode-kaliningrad-39.ru/]orikdok-5v-gorode-kaliningrad-39.ru[/url]
Где заказать диплом по актуальной специальности?
Заказать диплом ВУЗа по доступной цене возможно, обратившись к надежной специализированной фирме.: [url=http://diplom-insti.ru/]diplom-insti.ru[/url]
Заказать документ о получении высшего образования вы имеете возможность у нас в Москве. Мы оказываем услуги по продаже документов об окончании любых ВУЗов Российской Федерации. Даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документов работодателем, подозрений не появится. [url=http://ramonmestre.com.ar/2025/06/18/pokupka-diploma-vash-shag-k-novym-vozmozhnostjam-164/]ramonmestre.com.ar/2025/06/18/pokupka-diploma-vash-shag-k-novym-vozmozhnostjam-164[/url]
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании можем помочь. Купить диплом бакалавра в Курске – [url=http://diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-bakalavra-v-kurske/]diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-bakalavra-v-kurske[/url]
купить красный диплом [url=arus-diplom10.ru]купить красный диплом[/url] .
Купить диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по выгодным тарифам— [url=http://kazpages.ru/]kazpages.ru[/url]
This was beautiful Admin. Thank you for your reflections.
Teknoloji Kıbrıs Teknoloji Kıbrıs, Kıbrıs teknoloji, teknolojikibris, elektronik eşyalar, Kıbrıs ucuz ev eşyası, teknolojik aksesuar kıbrıs
Заказать диплом об образовании. Покупка подходящего диплома через надежную фирму дарит немало преимуществ. Такое решение позволяет сберечь время и серьезные деньги. [url=http://orikdok-v-gorode-vladikavkaz-15.ru/]orikdok-v-gorode-vladikavkaz-15.ru[/url]
купить диплом где можно [url=www.arus-diplom4.ru]купить диплом где можно[/url] .
купить диплом вуза недорого [url=https://arus-diplom7.ru]https://arus-diplom7.ru[/url] .
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1074 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom13.ru/]На сайте[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4449 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom12.ru/]Узнать подробнее[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом массажиста купить [url=http://arus-diplom9.ru/]диплом массажиста купить[/url] .
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам. Покупка диплома, который подтверждает обучение в университете, – это выгодное решение. Заказать диплом любого университета: [url=http://pc2163.com/viewtopic.php?t=326829/]pc2163.com/viewtopic.php?t=326829[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4963 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf17.ru/]Звоните[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2676 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf21.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании Москва[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3599 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf20.ru/]Узнать условия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3855 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf18.ru/]Где купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4409 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf17.ru/]На этой странице[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом врача [url=arus-diplom3.ru]arus-diplom3.ru[/url] .
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании [url=http://www.arus-diplom5.ru]купить диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании[/url] .
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Купить диплом любого университета:
[url=http://kueda-rmc.ru/vmk/dialog/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=58129/]kueda-rmc.ru/vmk/dialog/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=58129[/url]
купить диплом оригинал гознак [url=https://arus-diplom8.ru/]купить диплом оригинал гознак[/url] .
Купить диплом ВУЗа по выгодной стоимости можно, обратившись к проверенной специализированной компании. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании: [url=http://cyberdefenseprofessionals.com/companies/premialnie-diplom-24/]cyberdefenseprofessionals.com/companies/premialnie-diplom-24[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1024 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom10.ru/]Купить диплом специалиста недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1897 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom14.ru/]Купить диплом института[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, которые находятся в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Дипломы и аттестаты печатаются на бумаге высшего качества: [url=http://heyrodisscusion.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=3605/]heyrodisscusion.listbb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=10&t=3605[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1539 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom12.ru/]Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 958 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom11.ru/]Где купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2344 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf21.ru/]Купить диплом Россия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1320 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf19.ru/]Купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1485 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf20.ru/]Диплом высшего образования купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа!
Мы можем предложить дипломы любой профессии по выгодным тарифам— [url=http://diplomovoz.ru/]diplomovoz.ru[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4376 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf18.ru/]Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4090 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf17.ru/]Купить диплом университета в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом в мурманске [url=www.arus-diplom4.ru/]купить диплом в мурманске[/url] .
купить диплом об окончании училища [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru]купить диплом об окончании училища[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в кемерово [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru/]www.arus-diplom21.ru/[/url] .
Приобрести диплом вы имеете возможность через официальный портал компании. [url=http://boyara-analia.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=1283/]boyara-analia.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=7&t=1283[/url]
диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить [url=https://www.arus-diplom23.ru]диплом высшего образования с занесением в реестр купить[/url] .
диплом купить проведенный [url=arus-diplom22.ru]диплом купить проведенный[/url] .
Приобретение документа о высшем образовании через надежную фирму дарит ряд плюсов. Заказать диплом: [url=http://jagplay.ekafe.ru/viewtopic.php?f=22&t=11840]jagplay.ekafe.ru/viewtopic.php?f=22&t=11840[/url]
купить диплом без занесения в реестр [url=https://arus-diplom21.ru/]купить диплом без занесения в реестр[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4915 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom15.ru/]Купить диплом университета[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3052 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak1.ru/]Купить диплом университета[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4978 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom.su/]Купить диплом специалиста недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3142 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom1.ru/]Перейти[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Yazınız için teşekkürler. Bu bilgiler ışığında nice insanlar bilgilenmiş olacaktır.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3643 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak.su/]Где купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3450 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit.su/]Купить диплом специалиста недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом купить с внесением в реестр [url=www.arus-diplom24.ru/]диплом купить с внесением в реестр[/url] .
купить диплом техникума в москве [url=https://www.arus-diplom10.ru]https://www.arus-diplom10.ru[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2687 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit3.ru/]Перейти[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем документы об окончании любых университетов Российской Федерации. Документы производятся на настоящих бланках. [url=http://fdjobvacancies.com/employer/radiplomy/]fdjobvacancies.com/employer/radiplomy[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1651 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak1.ru/]Купить диплом института образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1673 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak.su/]Купить диплом института высшего образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2378 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom1.ru/]Купить дипломы о высшем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4841 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit1.ru/]Здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом о среднем купить [url=https://www.arus-diplom8.ru]диплом о среднем купить[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1551 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit3.ru/]Купить диплом Украина[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые расположены на территории всей Российской Федерации. Купить диплом университета:
[url=http://jobasjob.com/companies/diplomiki/]купить аттестаты гознак за 11 класс[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3956 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit2.ru/]Диплом об образовании купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Приобрести диплом на заказ в Москве возможно используя официальный сайт компании. [url=http://vared.flyboard.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1147/]vared.flyboard.ru/viewtopic.php?f=1&t=1147[/url]
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1492 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak2.ru/]Где можно купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4579 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom15.ru/]Купить дипломы о высшем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
новый диплом купить [url=http://arus-diplom6.ru/]http://arus-diplom6.ru/[/url] .
купить аттестат 11 класса в москве [url=http://arus-diplom24.ru/]http://arus-diplom24.ru/[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в украине [url=arus-diplom35.ru]arus-diplom35.ru[/url] .
купить диплом оригинал [url=www.arus-diplom7.ru]www.arus-diplom7.ru[/url] .
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак [url=arus-diplom22.ru]где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1922 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit2.ru/]Купить диплом института образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат 10 11 класса [url=http://arus-diplom24.ru]купить аттестат 10 11 класса[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4343 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak3.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании Украины[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2598 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom3.ru/]Купить диплом университета[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3016 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak4.ru/]Узнать условия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4972 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom2.ru/]Где купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1074 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit5.ru/]Купить дипломы вуза о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат 11 класс украина [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru]купить аттестат 11 класс украина[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс тирасполь [url=https://www.arus-diplom25.ru]купить аттестаты за 11 класс тирасполь[/url] .
купить диплом зарегистрированный в реестре [url=arus-diplom35.ru]arus-diplom35.ru[/url] .
диплом в самаре купить [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru/]диплом в самаре купить[/url] .
Nice post. I learn something totally new and challenging on websites
I just like the helpful information you provide in your articles
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4874 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak3.ru/]Купить диплом Киев[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2886 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit6.ru/]Купить диплом о образовании недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестаты за 11 класс в томске [url=www.arus-diplom22.ru/]www.arus-diplom22.ru/[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2049 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak4.ru/]Пишите[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4062 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom3.ru/]Купить диплом института образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр [url=www.arus-diplom34.ru/]купить диплом в архангельске с занесением в реестр[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4962 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit4.ru/]Купить диплом института высшего образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3377 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit5.ru/]Где можно купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом купить в реестре [url=https://arus-diplom35.ru/]диплом купить в реестре[/url] .
купить диплом о среднем [url=www.arus-diplom7.ru]купить диплом о среднем[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3908 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom4.ru/]Здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2969 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom5.ru/]Купить диплом с занесением[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы готовы предложить документы ВУЗов, которые находятся в любом регионе России. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://lavoroadesso.com/employer/ukrdiplom/]купить аттестаты за 11 класс недорого[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2109 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit7.ru/]Купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2214 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom5.ru/]Купить срочно диплом о высшем образовании вуза[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестаты за 11 класс в чите 1999 [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru]http://arus-diplom23.ru[/url] .
купить диплом вуза с занесением в реестр [url=https://arus-diplom35.ru]купить диплом вуза с занесением в реестр[/url] .
Приобрести диплом ВУЗа!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по приятным ценам— [url=http://ukr-diplom.ru/]ukr-diplom.ru[/url]
Sitenizin tasarımı da içerikleriniz de harika, özellikle içerikleri adım adım görsellerle desteklemeniz çok başarılı emeğinize sağlık.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3352 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak10.ru/]Купить диплом Украины[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4133 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak9.ru/]Купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 класс в вологде [url=http://arus-diplom24.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс в вологде[/url] .
законно купить аттестат за 11 класс [url=arus-diplom22.ru]законно купить аттестат за 11 класс[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3199 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak7.ru/]Диплом об образовании купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2054 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak8.ru/]Обращайтесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2023 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit8.ru/]Где купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1068 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak5.ru/]Где купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые расположены в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Купить диплом университета:
[url=http://fittact.vip/read-blog/929_skolko-stoit-kupit-attestat-11-klassa.html/]купить аттестат егэ 11 класс[/url]
купить диплом об окончании 11 классов [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru]http://arus-diplom8.ru[/url] .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по выгодным ценам. Купить диплом доктора наук — [url=http://kyc-diplom.com/diplom-doktora-nauk.html/]kyc-diplom.com/diplom-doktora-nauk.html[/url]
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
I truly appreciate your technique of writing a blog. I added it to my bookmark site list and will
I like the efforts you have put in this, regards for all the great content.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3109 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak9.ru/]Купить срочно диплом о высшем образовании вуза[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1453 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak8.ru/]Купить дипломы[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Çok yararlı bi yazı olmuş hocam teşekkür ederim .Sizin yazılarınızı beğenerek okuyorum elinize sağlık.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3746 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak6.ru/]Купить диплом недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2259 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit8.ru/]Узнать подробнее[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1085 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit9.ru/]Купить диплом об образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат 11 классов в калининграде [url=arus-diplom22.ru]arus-diplom22.ru[/url] .
купить диплом спб с занесением в реестр [url=https://arus-diplom32.ru/]https://arus-diplom32.ru/[/url] .
купить аттестат 10 11 классов [url=arus-diplom25.ru]купить аттестат 10 11 классов[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru/]купить аттестаты за 11 класс москва[/url] .
купить диплом с проводкой моего [url=www.arus-diplom31.ru/]купить диплом с проводкой моего[/url] .
Приобрести диплом на заказ в Москве возможно через сайт компании. [url=http://ceecentre.org/employer/78231/education-ua/]ceecentre.org/employer/78231/education-ua[/url]
купить аттестат 11 в сыктывкаре [url=https://www.arus-diplom23.ru]https://www.arus-diplom23.ru[/url] .
купить аттестат цена [url=https://arus-diplom8.ru/]купить аттестат цена[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр украина [url=www.arus-diplom35.ru]купить диплом с занесением в реестр украина[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр чита [url=www.arus-diplom34.ru]www.arus-diplom34.ru[/url] .
купить недорого аттестат 11 класс [url=http://www.arus-diplom25.ru]купить недорого аттестат 11 класс[/url] .
Приобрести диплом университета поспособствуем. Купить диплом в городе Саратов – [url=http://diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-saratov/]diplomybox.com/kupit-diplom-saratov[/url]
This was beautiful Admin. Thank you for your reflections.
For the reason that the admin of this site is working, no uncertainty very quickly it will be renowned, due to its quality contents.
можно ли в красноярске купить диплом [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru/]можно ли в красноярске купить диплом[/url] .
купить диплом спб с занесением в реестр [url=arus-diplom33.ru]arus-diplom33.ru[/url] .
купить аттестат 11 классов в спб [url=https://www.arus-diplom22.ru]купить аттестат 11 классов в спб[/url] .
Мы можем предложить документы учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей России. Приобрести диплом ВУЗа:
[url=http://pro-eltern.de/read-blog/727/]как купить аттестат за 11 класс спб[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4489 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak11.ru/]Купить диплом Украина[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Explore the world of BitStarz, claim your welcome bonus of 5 BTC and 180 free spins, awarded Best Casino multiple times. Stay connected through official mirror.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2543 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf26.ru/]Диплом купить Москва[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4681 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit10.ru/]На сайте[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4935 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom16.ru/]Купить диплом недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4549 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf25.ru/]Узнать условия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2789 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor22.ru/]Купить диплом нового образца[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2452 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom22.ru/]По ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
аттестат за 11 купить спб [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru/]аттестат за 11 купить спб[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3963 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak11.ru/]Узнать условия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4830 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf26.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2860 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit10.ru/]Где можно купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1411 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom16.ru/]Купить диплом института[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2111 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf25.ru/]Диплом купить Москва[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4436 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor22.ru/]Купить диплом университета в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4876 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom22.ru/]Где купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3524 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom21.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем техническом образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 классов с занесением в реестр в москве [url=www.arus-diplom24.ru/]www.arus-diplom24.ru/[/url] .
Купить диплом на заказ в Москве возможно используя сайт компании. [url=http://ipora-vivirbien.com/kupit-diplom-oficialno-i-bez-riska-237/]ipora-vivirbien.com/kupit-diplom-oficialno-i-bez-riska-237[/url]
купить аттестат в воронеже [url=http://www.arus-diplom8.ru]купить аттестат в воронеже[/url] .
купить школьный аттестат за 11 классов [url=http://www.arus-diplom7.ru]купить школьный аттестат за 11 классов[/url] .
аттестат 11 класс 2014 купить [url=www.arus-diplom22.ru/]аттестат 11 класс 2014 купить[/url] .
Play better after reading this aviator game review
купить красный аттестаты за 11 [url=www.arus-diplom23.ru/]купить красный аттестаты за 11[/url] .
как купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр цена в [url=http://www.arus-diplom34.ru]как купить диплом техникума с занесением в реестр цена в[/url] .
как купить легально диплом о высшем образовании [url=arus-diplom33.ru]как купить легально диплом о высшем образовании[/url] .
купить аттестат за 10 11 классы [url=www.arus-diplom22.ru]купить аттестат за 10 11 классы[/url] .
купить обложку аттестата за 11 [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru/]купить обложку аттестата за 11[/url] .
хочу купить аттестат 11 классов [url=www.arus-diplom24.ru]www.arus-diplom24.ru[/url] .
Enjoy uninterrupted play thanks to a casino mirror
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2540 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak12.ru/]Купить дипломы[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1335 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom7.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1425 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor24.ru/]Где купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1818 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf28.ru/]Диплом колледжа купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3558 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom17.ru/]Купить диплом Украины[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена купить диплом с занесением в реестр цена .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3424 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom23.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр [url=https://www.arus-diplom34.ru]купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании с занесением в реестр[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс г облучье [url=https://www.arus-diplom21.ru]https://www.arus-diplom21.ru[/url] .
где купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс [url=arus-diplom10.ru]где купить школьный аттестат за 11 класс[/url] .
можно ли купить диплом в реестре [url=www.forum.good-cook.ru/user227672.html]можно ли купить диплом в реестре[/url] .
аттестат за 11 купить спб [url=https://arus-diplom22.ru]аттестат за 11 купить спб[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2393 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak12.ru/]Купить диплом о образовании недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3015 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom7.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании Украины[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1113 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf28.ru/]Диплом высшего образования купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4419 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor24.ru/]На этой странице[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2723 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor23.ru/]Мы поможем[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2036 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit11.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
новый диплом купить [url=www.arus-diplom8.ru]www.arus-diplom8.ru[/url] .
Мы предлагаем документы учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://mosros.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=924&sid=82b91fff056a68d2a4c21315c217c78c/]купить аттестат за 11 классов в кемерово[/url]
купить легально диплом [url=www.arus-diplom35.ru]купить легально диплом[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3446 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom24.ru/]Диплом высшего образования купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
аттестат 11 класс купить тюмень [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru]аттестат 11 класс купить тюмень[/url] .
купить диплом с внесением в реестр [url=http://arus-diplom32.ru]купить диплом с внесением в реестр[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в партизанске [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru/]купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в партизанске[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестры [url=www.arus-diplom31.ru]купить диплом с занесением в реестры[/url] .
Купить диплом под заказ в столице вы можете через сайт компании. [url=http://poeskovek.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=752/]poeskovek.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=2&t=752[/url]
кемерово купить аттестат за 11 [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru/]кемерово купить аттестат за 11[/url] .
где можно купить аттестат 11 классов липецк [url=https://arus-diplom10.ru]где можно купить аттестат 11 классов липецк[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в спб [url=https://www.detskiy-mir.net/user/iliaanisimov]https://www.detskiy-mir.net/user/iliaanisimov[/url] .
💼 Микрокредит займ на бизнес
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр [url=www.arus-diplom34.ru/]купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр[/url] .
диплом механика купить [url=www.arus-diplom6.ru/]www.arus-diplom6.ru/[/url] .
диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить [url=arus-diplom35.ru]диплом о высшем образовании с проводкой купить[/url] .
Мы можем предложить документы университетов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа:
[url=http://dimitrii.flybb.ru/viewtopic.php?f=29&t=1540/]где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан[/url]
Сайт Lucky Star и 1WIN дают игрокам шанс выиграть в Лаки Джет.
купить аттестат за 11 классов и егэ [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru/]http://arus-diplom23.ru/[/url] .
Casino mirror enhances session stability
купить аттестат 1995 11 классов [url=https://www.arus-diplom24.ru]купить аттестат 1995 11 классов[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 классов нижневартовск [url=www.arus-diplom25.ru]www.arus-diplom25.ru[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1399 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom8.ru/]По ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2610 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor26.ru/]Диплом колледжа купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1530 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit12.ru/]По ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Заказать диплом на заказ вы можете через официальный сайт компании. [url=http://businessconsultbg.com/employer/diploms-ukraine/]businessconsultbg.com/employer/diploms-ukraine[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1904 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak13.ru/]Купить диплом Украины[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1124 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom25.ru/]Купить диплом Россия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2577 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf29.ru/]Диплом института купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3255 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor25.ru/]Пишите в личные сообщения[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3482 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom18.ru/]Купить дипломы[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр ростов [url=https://arus-diplom35.ru/]купить диплом с занесением в реестр ростов[/url] .
купить диплом в нижнем новгороде [url=https://arus-diplom8.ru/]https://arus-diplom8.ru/[/url] .
купить аттестат 11 [url=https://www.arus-diplom21.ru]купить аттестат 11[/url] .
Harika bir paylaşım, özellikle konunun önemli detayları oldukça net bir şekilde açıklanmış. İnsanları çeşitli karmaşık anahtar kelimelerle yormak yerine, okumaktan keyif alacağı içerikler her zaman daha iyidir. Kaliteli paylaşım adına teşekkür eder, paylaşımlarınızın devamını sabırsızlıkla beklerim.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1508 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom8.ru/]Пишите нам[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4707 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak13.ru/]Где купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4092 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor26.ru/]Купить диплом академии[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1426 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit12.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании недорого[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4971 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://poligraf29.ru/]Открыть[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2408 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom26.ru/]Купить дипломы[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1793 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor25.ru/]Уточнить здесь[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4122 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom18.ru/]Узнать подробнее[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы [url=www.arus-diplom31.ru/]купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр отзывы[/url] .
купить проведенный диплом одно [url=http://www.arus-diplom34.ru]купить проведенный диплом одно[/url] .
аттестат за 11 классов купить в алматы [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru]аттестат за 11 классов купить в алматы[/url] .
купить аттестаты гознак [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru]купить аттестаты гознак[/url] .
Заказать диплом об образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любых профессий по приятным тарифам— [url=http://vacshidiplom.com/]vacshidiplom.com[/url]
диплом купить колледжа [url=www.arus-diplom8.ru/]диплом купить колледжа[/url] .
Заказать диплом вы сможете через официальный портал компании. [url=http://bodybuilding.net/members/worksale.html/]bodybuilding.net/members/worksale.html[/url]
Мы готовы предложить документы институтов, которые находятся в любом регионе Российской Федерации. Заказать диплом любого ВУЗа:
[url=http://psalmtechproperties.com/profile/thanharrowood0/]купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в партизанске[/url]
Your online casino experience starts with a mirror
диплом купить с проводкой [url=www.arus-diplom35.ru]диплом купить с проводкой[/url] .
купить диплом массажиста [url=http://arus-diplom6.ru]http://arus-diplom6.ru[/url] .
где купить аттестат 11 класса [url=www.arus-diplom24.ru/]где купить аттестат 11 класса[/url] .
купить диплом украины с занесением в реестр [url=arus-diplom31.ru]arus-diplom31.ru[/url] .
диплом купить сколько стоит [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru/]диплом купить сколько стоит[/url] .
купить диплом занесением реестр киев [url=arus-diplom34.ru]arus-diplom34.ru[/url] .
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр [url=http://arus-diplom35.ru]http://arus-diplom35.ru[/url] .
Very well presented. Every quote was awesome and thanks for sharing the content. Keep sharing and keep motivating others.
Hi there to all, for the reason that I am genuinely keen of reading this website’s post to be updated on a regular basis. It carries pleasant stuff.
аттестат 11 купить [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru]аттестат 11 купить[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1070 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit13.ru//]Высшее образование купить диплом с занесением[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1352 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit15.ru/]По ссылке[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1914 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom19.ru/]Купить диплом института образования[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3687 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom22.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4382 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomygoznak14.ru/]Перейти[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1207 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://kupludiplom9.ru/]Купить срочно диплом о высшем образовании вуза[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить проведенный диплом вуза [url=www.arus-diplom33.ru/]www.arus-diplom33.ru/[/url] .
купить аттестат школы за 11 lr 50 [url=www.arus-diplom25.ru/]www.arus-diplom25.ru/[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4787 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom23.ru/]Куплю диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2295 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit15.ru/]Купить диплом с занесением[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 943 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://diplomykupit14.ru/]Диплом об образовании купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2440 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom19.ru/]Купить настоящий диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Family mediated matrimony traditions thrive on gulfshaadi.com.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3716 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://uadiplom22.ru/]Перейти[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в калуге [url=http://arus-diplom35.ru/]купить диплом с занесением в реестр в калуге[/url] .
купить диплом спб занесением реестр [url=https://www.arus-diplom32.ru]купить диплом спб занесением реестр[/url] .
где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак [url=arus-diplom9.ru]где купить аттестаты за 11 класс гознак[/url] .
диплом купить цена [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru/]диплом купить цена[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в ярославле [url=www.arus-diplom25.ru]купить аттестат за 11 классов в ярославле[/url] .
диплом с занесением в реестр купить [url=www.arus-diplom31.ru/]диплом с занесением в реестр купить[/url] .
где купить аттестат за 10 11 класс [url=https://arus-diplom9.ru/]где купить аттестат за 10 11 класс[/url] .
диплом в калуге купить [url=www.arus-diplom7.ru]www.arus-diplom7.ru[/url] .
купить диплом внесенный в реестр [url=https://arus-diplom35.ru/]купить диплом внесенный в реестр[/url] .
где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru/]где можно купить аттестаты 11 класс в таджикистан в иркутске[/url] .
диплом о высшем образовании старого образца купить [url=https://www.arus-diplom8.ru]диплом о высшем образовании старого образца купить[/url] .
Заказать диплом института!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам— [url=http://seo-elita.ru/]seo-elita.ru[/url]
как купить диплом занесенный в реестр [url=www.arus-diplom32.ru]как купить диплом занесенный в реестр[/url] .
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3035 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom30.ru/]Купить дипломы о высшем образовании в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3436 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor30.ru/]Где купить диплом о среднем специальном образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом легальный [url=http://arus-diplom33.ru]купить диплом легальный[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3895 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor29.ru/]Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 класс краснодаре [url=http://www.arus-diplom21.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс краснодаре[/url] .
купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru/]купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс[/url] .
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Приобрести диплом любого ВУЗа:
[url=http://korrespondentweek.ru/kak-kupit-diplom-s-garantiey-podlinnosti/]купить аттестаты за 11 класс[/url]
аттестат купить 11 кл [url=https://arus-diplom10.ru/]аттестат купить 11 кл[/url] .
Unlock new levels in Lucky Jet – everyone’s talking about it.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3148 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom30.ru/]Купить диплом академии[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4725 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor28.ru/]Диплом купить[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2639 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor32.ru/]Купить диплом о среднем техническом образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1080 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor30.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании Москва[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
екатеринбург купить диплом в реестр [url=https://www.arus-diplom35.ru]екатеринбург купить диплом в реестр[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4212 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom28.ru/]Звоните[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр [url=http://arus-diplom34.ru/]купить диплом медсестры с занесением в реестр[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2835 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor29.ru/]Где можна купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
диплом психолога купить [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru/]диплом психолога купить[/url] .
купить аттестат 11 классов в челябинске [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru]http://arus-diplom22.ru[/url] .
за сколько можно купить аттестат за 11 классов [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru]за сколько можно купить аттестат за 11 классов[/url] .
москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр [url=arus-diplom32.ru]москва купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр[/url] .
купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в москве [url=http://arus-diplom31.ru]купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр в москве[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в новосибирске [url=http://arus-diplom9.ru/]купить аттестаты за 11 классов в новосибирске[/url] .
аттестат купить за 11 классов в москве [url=http://arus-diplom21.ru]аттестат купить за 11 классов в москве[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в новосибирске [url=http://www.arus-diplom24.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс в новосибирске[/url] .
Мы можем предложить документы институтов, которые расположены на территории всей РФ. Купить диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://ashkert.am/???????-?????/diplomiki/]купить аттестаты за 11 классов в екатеринбурге[/url]
Works globally: casino mirror links for Europe, Asia, and Africa.
где можно купить аттестаты 11 [url=www.arus-diplom9.ru/]где можно купить аттестаты 11[/url] .
купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс [url=https://arus-diplom21.ru]купить аттестат 10 и 11 класс[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 класс 1998 года [url=www.arus-diplom22.ru/]купить аттестат за 11 класс 1998 года[/url] .
диплом в перми купить [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru]диплом в перми купить[/url] .
купить диплом с проводкой одно [url=www.arus-diplom35.ru/]купить диплом с проводкой одно[/url] .
купить аттестат в москве за 11 класс [url=arus-diplom21.ru]купить аттестат в москве за 11 класс[/url] .
купить бланк аттестата за 11 класс [url=arus-diplom25.ru]купить бланк аттестата за 11 класс[/url] .
купить проведенный аттестат за 11 класс [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru]купить проведенный аттестат за 11 класс[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск [url=https://arus-diplom31.ru/]купить диплом с занесением в реестр челябинск[/url] .
легальный диплом купить [url=https://arus-diplom32.ru]легальный диплом купить[/url] .
купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр [url=www.arus-diplom31.ru]купить диплом москва с занесением в реестр[/url] .
купить диплом в астрахани [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru/]купить диплом в астрахани[/url] .
сколько стоит аттестат 11 классов купить [url=http://arus-diplom24.ru/]http://arus-diplom24.ru/[/url] .
Приобрести диплом под заказ вы имеете возможность через сайт компании. [url=http://jobsleed.com/companies/education-ua/]jobsleed.com/companies/education-ua[/url]
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1424 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor31.ru/]Купить диплом вуза[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3818 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom32.ru/]Диплом цена[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4437 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom33.ru/]Купить диплом о высшем образовании[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1605 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor34.ru/]Купить государственный диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3752 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor36.ru/]Купить диплом об окончании института[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 10 11 класс отзывы [url=https://arus-diplom22.ru/]https://arus-diplom22.ru/[/url] .
купить диплом украина с занесением в реестр [url=www.arus-diplom35.ru/]www.arus-diplom35.ru/[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр самара [url=www.arus-diplom34.ru/]www.arus-diplom34.ru/[/url] .
купить легальный диплом колледжа [url=https://arus-diplom33.ru]купить легальный диплом колледжа[/url] .
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4123 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom36.ru/]Где купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить диплом техникума в реестре цена [url=http://msfofm.ru/forum/user/50253-vadyymemelnvv]купить диплом техникума в реестре цена[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в барнауле [url=https://arus-diplom10.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс в барнауле[/url] .
диплом высшего образования проведенный купить [url=https://arus-diplom34.ru]диплом высшего образования проведенный купить[/url] .
диплом о высшем образовании купить с занесением в реестр [url=https://www.arus-diplom31.ru]диплом о высшем образовании купить с занесением в реестр[/url] .
купить аттестат в челябинске [url=arus-diplom8.ru]купить аттестат в челябинске[/url] .
I very delighted to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for as well saved to fav
купить аттестат за 11 классов с занесением в реестр в москве [url=www.arus-diplom24.ru]www.arus-diplom24.ru[/url] .
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1144 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom33.ru/]Пишите[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2678 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor31.ru/]Купить диплом Россия[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов В киеве — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 4292 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom32.ru/]Купить диплом вуза[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Покупка дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2468 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://spbrcom35.ru/]Купить государственный диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 1208 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor36.ru/]Как купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
Мы предлагаем оформление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы гарантируем, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 3630 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor34.ru/]Диплом о высшем образовании купить в Москве[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 класс минск [url=https://arus-diplom23.ru/]https://arus-diplom23.ru/[/url] .
аттестаты купить [url=arus-diplom6.ru]аттестаты купить[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс в иркутске [url=http://arus-diplom22.ru]купить аттестаты за 11 класс в иркутске[/url] .
Мы предлагаем документы университетов, которые находятся на территории всей Российской Федерации. Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://turservisnews.ru/kachestvennyie-diplomyi-bez-posrednikov/]купить аттестат 10 11 класса[/url]
Купить диплом можно используя сайт компании. [url=http://ppenet.com/employer/diploms-ukraine/]ppenet.com/employer/diploms-ukraine[/url]
купить диплом без занесения в реестр [url=https://arus-diplom35.ru]купить диплом без занесения в реестр[/url] .
где купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru]где купить чистый аттестат за 11 класс[/url] .
аттестаты купить в москве за 11 класс [url=http://www.arus-diplom25.ru]аттестаты купить в москве за 11 класс[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр барнаул [url=http://arus-diplom34.ru]купить диплом с занесением в реестр барнаул[/url] .
Мы изготавливаем дипломы психологов, юристов, экономистов и любых других профессий по приятным ценам. Купить диплом о неполном образовании — [url=http://kyc-diplom.com/diplom-o-nepolnom-obrazovanii.html/]kyc-diplom.com/diplom-o-nepolnom-obrazovanii.html[/url]
как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр [url=https://www.arus-diplom35.ru]как купить диплом о высшем образовании с занесением в реестр[/url] .
Мы можем предложить документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных на территории всей России. Купить диплом ВУЗа:
[url=http://avtolux48.ru/people/user/374/blog/12180/]купить аттестаты за 11 класс приднестровье тирасполе[/url]
Оформиление дипломов ВУЗов по всей Украине — с печатями, подписями, приложением и возможностью архивной записи (по запросу).
Документ максимально приближен к оригиналу и проходит визуальную проверку.
Мы даем гарантию, что в случае проверки документа, подозрений не возникнет.
– Конфиденциально
– Доставка 3–7 дней
– Любая специальность
Уже более 2399 клиентов воспользовались услугой — теперь ваша очередь.
[url=http://inforepetitor37.ru/]Где можна купить диплом[/url] — ответим быстро, без лишних формальностей.
купить аттестат за 11 классов в новосибирске [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru]http://arus-diplom23.ru[/url] .
купить аттестат 11 классов тюмень [url=http://www.arus-diplom22.ru]http://www.arus-diplom22.ru[/url] .
купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр [url=http://arus-diplom31.ru]купить диплом высшем образовании занесением реестр[/url] .
купить диплом в перми [url=http://arus-diplom8.ru]купить диплом в перми[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в реестр отзывы спб [url=http://arus-diplom24.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс с занесением в реестр отзывы спб[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 классов в владивостоке [url=http://www.arus-diplom22.ru]http://www.arus-diplom22.ru[/url] .
Заказать диплом на заказ можно через сайт компании. [url=http://horecaclub.it/read-blog/11919_kupit-attestat-posle-9-klassa.html/]horecaclub.it/read-blog/11919_kupit-attestat-posle-9-klassa.html[/url]
купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург [url=http://arus-diplom34.ru/]купить диплом с занесением в реестр оренбург[/url] .
купить диплом занесением реестр киев [url=http://www.arus-diplom33.ru]http://www.arus-diplom33.ru[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 класс [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru/]http://arus-diplom7.ru/[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 классов в кропоткине [url=https://arus-diplom25.ru]купить аттестаты за 11 классов в кропоткине[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в москве [url=http://arus-diplom33.ru/]купить диплом с занесением в реестр в москве[/url] .
диплом как купить [url=http://arus-diplom6.ru]http://arus-diplom6.ru[/url] .
купить диплом ссср [url=www.arus-diplom8.ru/]купить диплом ссср[/url] .
купить проведенный диплом [url=www.arus-diplom35.ru/]купить проведенный диплом[/url] .
купить копию аттестата за 11 класс [url=https://arus-diplom23.ru]https://arus-diplom23.ru[/url] .
купил аттестат за 11 [url=http://arus-diplom24.ru]http://arus-diplom24.ru[/url] .
купить диплом в уфе с реестром [url=arus-diplom34.ru]arus-diplom34.ru[/url] .
купить диплом с занесением в реестр в кемерово [url=http://arus-diplom33.ru]http://arus-diplom33.ru[/url] .
Купить диплом университета!
Мы готовы предложить дипломы любой профессии по доступным тарифам— [url=http://diplomp-irkutsk.ru/]diplomp-irkutsk.ru[/url]
купить диплом с занесением в реестр новокузнецке [url=https://arus-diplom32.ru]купить диплом с занесением в реестр новокузнецке[/url] .
Мы готовы предложить документы любых учебных заведений, расположенных в любом регионе РФ. Заказать диплом любого университета:
[url=http://p91648f6.beget.tech/2025/07/09/diplomy-dlya-grazhdan-rf-i-sng.html/]купить аттестаты за 11 класс украина[/url]
Join your casino via a private mirror link
бланк аттестат за 11 класс купить в [url=www.arus-diplom23.ru]бланк аттестат за 11 класс купить в[/url] .
купить диплом с регистрацией [url=https://arus-diplom31.ru/]купить диплом с регистрацией[/url] .
диплом психолога купить [url=http://arus-diplom7.ru]диплом психолога купить[/url] .
купить диплом с реестром цена [url=www.arus-diplom34.ru/]купить диплом с реестром цена[/url] .
диплом занесен в реестр купить [url=https://arus-diplom35.ru/]диплом занесен в реестр купить[/url] .
Приобрести диплом о высшем образовании!
Мы изготавливаем дипломы любой профессии по приятным тарифам— [url=http://masterdiplomov.ru/]masterdiplomov.ru[/url]
Мы готовы предложить документы университетов, расположенных на территории всей РФ. Заказать диплом о высшем образовании:
[url=http://vulnerableyouthjobs.ca/companies/diplomiki/]купить аттестат 11 в сыктывкаре[/url]
купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр [url=arus-diplom33.ru]купить диплом о средне специальном образовании реестр[/url] .
где купить аттестат [url=www.arus-diplom8.ru]где купить аттестат[/url] .
купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в москве [url=www.arus-diplom21.ru/]купить аттестаты за 11 вечерней школе в москве[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 класс 2014 года [url=www.arus-diplom22.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс 2014 года[/url] .
купить аттестат за 11 класс в астрахани [url=http://www.arus-diplom24.ru]купить аттестат за 11 класс в астрахани[/url] .
где в омске купить аттестат 11 классов [url=http://arus-diplom23.ru/]где в омске купить аттестат 11 классов[/url] .
I appreciate the step-by-step guide.
Thanks for the valuable content.
aramalarım sonunda buraya geldim ve kesinlikle işime yarayan bir makale oldu. teşekkür ederim
LeonBet ist mehr als nur ein Wettanbieter.
Makaleniz açıklayıcı yararlı anlaşılır olmuş ellerinize sağlık
Avoid losing progress with a stable casino mirror
Watch your winnings soar in the Aviator game.
Experience quality gaming at Bitstarz Casino.
Fantastic read! 👏 I really appreciate how clearly you explained the topic—your writing not only shows expertise but also makes the subject approachable for a wide audience. It’s rare to come across content that feels both insightful and practical at the same time. At explodingbrands.de we run a growing directory site in Germany that features businesses from many different categories. That’s why I truly value articles like yours, because they highlight how knowledge and visibility can create stronger connections between people, services, and opportunities.Keep up the great work—I’ll definitely be checking back for more of your insights! 🚀
Streamlined cashier flows at BitStarz Casino help you deposit or withdraw in minutes, tracking status right from your profile.
Актуальное зеркало казино — без лишних настроек
Yolda kaldığınızda Bafra çekici ekibi en kısa sürede yanınızda olur. Bafra oto yol yardım hizmeti, hem şehir içi hem de şehirlerarası güvenli çözümler sunar. Bafra oto kurtarma, arızalı araçları güvenli şekilde taşır. Bafra oto yol yardım her zaman ulaşılabilir durumdadır.
Learn hotkeys inside the Aviator game and map them right after your Aviator game download.
Learn the Aviator game; get the clean Aviator game download.
Evaluate latency bursts in the Aviator game; reinstall from a clean Aviator game download if needed.
Learn bankroll discipline inside the Aviator game; use the trusted Aviator game download to set limits and play smoothly.
Explore beginner FAQs for the Aviator game and follow the official Aviator game download steps.
Practice exit drills for the Aviator game in demo; secure a reliable Aviator game download and simulate real stakes.
Keep a privacy audit schedule for the Aviator game; review it after each Aviator game download update.
Learn the Aviator game fast with win/loss tracking. Follow our Aviator game download checklist and build safer cashout habits.
Read patch notes for the Aviator game; refresh via official Aviator game download.
Protect your wallet data linked to the Aviator game by using a reputable Aviator game download.
Thank you for sharing such a well-structured and easy-to-digest post. It’s not always easy to find content that strikes the right balance between informative and engaging, but this piece really delivered. I appreciated how each section built on the last without overwhelming the reader. Even though I’ve come across similar topics before, the way you presented the information here made it more approachable. I’ll definitely be returning to this as a reference point. It’s the kind of post that’s genuinely helpful no matter your level of experience with the subject. Looking forward to reading more of your work—keep it up! profis-vor-ort.de
Lucky Jet game download provides mobile access to casino excitement.
Aviator game download guarantees access on any mobile device.
Good post! We will be linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the great writing
I’m often to blogging and i really appreciate your content. The article has actually peaks my interest. I’m going to bookmark your web site and maintain checking for brand spanking new information.